Phosphatidylethanolamine Metabolism in Health and Disease
- PMID: 26811286
- PMCID: PMC4778737
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2015.10.001
Phosphatidylethanolamine Metabolism in Health and Disease
Abstract
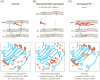
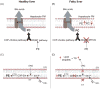
Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) is the second most abundant glycerophospholipid in eukaryotic cells. The existence of four only partially redundant biochemical pathways that produce PE, highlights the importance of this essential phospholipid. The CDP-ethanolamine and phosphatidylserine decarboxylase pathways occur in different subcellular compartments and are the main sources of PE in cells. Mammalian development fails upon ablation of either pathway. Once made, PE has diverse cellular functions that include serving as a precursor for phosphatidylcholine and a substrate for important posttranslational modifications, influencing membrane topology, and promoting cell and organelle membrane fusion, oxidative phosphorylation, mitochondrial biogenesis, and autophagy. The importance of PE metabolism in mammalian health has recently emerged following its association with Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, nonalcoholic liver disease, and the virulence of certain pathogenic organisms.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; CDP-ethanolamine; Parkinson's disease; autophagy; mitochondria; phosphatidylethanolamine; phosphatidylserine decarboxylase.
Copyright © 2016. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures


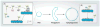

References
-
- Abbas N, Lucking CB, Ricard S, Durr A, Bonifati V, De Michele G, Bouley S, Vaughan JR, Gasser T, Marconi R, Broussolle E, Brefel-Courbon C, Harhangi BS, Oostra BA, Fabrizio E, Bohme GA, Pradier L, Wood NW, Filla A, Meco G, Denefle P, Agid Y, Brice A. A wide variety of mutations in the parkin gene are responsible for autosomal recessive parkinsonism in Europe. French Parkinson's Disease Genetics Study Group and the European Consortium on Genetic Susceptibility in Parkinson's Disease. Hum Mol Genet. 1999;8:567–574. - PubMed
-
- Achleitner G, Gaigg B, Krasser A, Kainersdorfer E, Kohlwein SD, Perktold A, Zellnig G, Daum G. Association between the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria of yeast facilitates interorganelle transport of phospholipids through membrane contact. Eur J Biochem. 1999;264:545–553. - PubMed
-
- Achleitner G, Zweytick D, Trotter PJ, Voelker DR, Daum G. Synthesis and intracellular transport of aminoglycerophospholipids in permeabilized cells of the yeast, Saccharomycescerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:29836–29842. - PubMed
-
- Acín-Pérez R, Fernández-Silva P, Peleato ML, Pérez-Martos A, Enriquez JA. Respiratory active mitochondrial supercomplexes. Mol Cell. 2008;32:529–539. - PubMed
-
- Alexander C, Votruba M, Pesch UE, Thiselton DL, Mayer S, Moore A, Rodriguez M, Kellner U, Leo-Kottler B, Auburger G, Bhattacharya SS, Wissinger B. OPA1, encoding a dynamin-related GTPase, is mutated in autosomal dominant optic atrophy linked to chromosome 3q28. Nat Genet. 2000;26:211–215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

