Biogeography of a human oral microbiome at the micron scale
- PMID: 26811460
- PMCID: PMC4760785
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1522149113
Biogeography of a human oral microbiome at the micron scale
Abstract
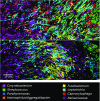
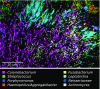
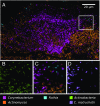
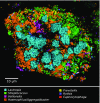
The spatial organization of complex natural microbiomes is critical to understanding the interactions of the individual taxa that comprise a community. Although the revolution in DNA sequencing has provided an abundance of genomic-level information, the biogeography of microbiomes is almost entirely uncharted at the micron scale. Using spectral imaging fluorescence in situ hybridization as guided by metagenomic sequence analysis, we have discovered a distinctive, multigenus consortium in the microbiome of supragingival dental plaque. The consortium consists of a radially arranged, nine-taxon structure organized around cells of filamentous corynebacteria. The consortium ranges in size from a few tens to a few hundreds of microns in radius and is spatially differentiated. Within the structure, individual taxa are localized at the micron scale in ways suggestive of their functional niche in the consortium. For example, anaerobic taxa tend to be in the interior, whereas facultative or obligate aerobes tend to be at the periphery of the consortium. Consumers and producers of certain metabolites, such as lactate, tend to be near each other. Based on our observations and the literature, we propose a model for plaque microbiome development and maintenance consistent with known metabolic, adherence, and environmental considerations. The consortium illustrates how complex structural organization can emerge from the micron-scale interactions of its constituent organisms. The understanding that plaque community organization is an emergent phenomenon offers a perspective that is general in nature and applicable to other microbiomes.
Keywords: biofilm; imaging; microbial ecology; microscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
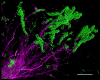
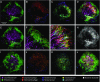
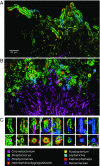

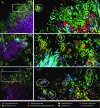
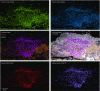
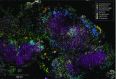
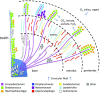
Comment in
-
Microbial ecology: FISHing in the oral microbiota.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016 Mar;14(3):132-3. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.21. Epub 2016 Feb 8. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26853115 No abstract available.
-
Oral Biofilm Architecture at the Microbial Scale.Trends Microbiol. 2016 Apr;24(4):246-248. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2016.02.013. Epub 2016 Mar 5. Trends Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26962018
References
-
- Diaz PI, Zilm PS, Rogers AH. Fusobacterium nucleatum supports the growth of Porphyromonas gingivalis in oxygenated and carbon-dioxide-depleted environments. Microbiology. 2002;148(Pt 2):467–472. - PubMed
-
- Jakubovics NS. Intermicrobial interactions as a driver for community composition and stratification of oral biofilms. J Mol Biol. 2015;427(23):3662–3675. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

