Bioinformatics analysis of hepatitis C virus genotype 2a-induced human hepatocellular carcinoma in Huh7 cells
- PMID: 26811688
- PMCID: PMC4712971
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S91748
Bioinformatics analysis of hepatitis C virus genotype 2a-induced human hepatocellular carcinoma in Huh7 cells
Abstract
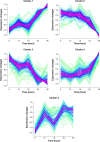
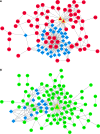
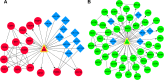
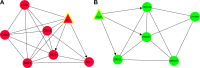
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a liver cancer that could be induced by hepatitis C virus genotype 2a Japanese fulminant hepatitis-1 (JFH-1) strain. The aim of this study was to investigate the molecular mechanisms of HCC. The microarray data GSE20948 includes 14 JFH-1- and 14 mock (equal volume of medium [control])-infected Huh7 samples. The data were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus. After data processing, soft cluster analyses were performed to identify co-regulated genes with similar temporal expression patterns. Functional and pathway enrichment analyses, as well as functional annotation analysis, were performed. Subsequently, combined networks of protein-protein interaction network, microRNA regulatory network, and transcriptional regulatory network were constructed. Hub nodes, modules, and five clusters of co-regulated genes were also identified. In total, 173 up and 207 down co-regulated genes were separately identified in JFH-1-infected Huh7 cells compared with those of control cells. Functional enrichment analysis indicated that up co-regulated genes were related to skeletal system morphogenesis and neuron differentiation and down co-regulated genes were related to steroid/cholesterol/sterol metabolisms. Hub genes (such as IRF1, GBP1, ICAM1, Foxa1, DHCR7, HMGCS2, and MSMO1) were identified. Transcription factors IRF1 and Foxa1 were the targets of miR-130a, miR-17-5p, and miR-20a. PPARGC1A was targeted by miR-29 family, and MSMO1 was the target of miR-23 family. Hub nodes (such as IRF1, GBP1, ICAM1, Foxa1, DHCR7, HMGCS2, and MSMO1) and microRNAs might be used as candidate biomarkers of JFH-1-infected HCC.
Keywords: co-regulated genes; combined network; microRNAs; soft cluster analysis; transcription factors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of potential miRNA-mRNA regulatory network contributing to pathogenesis of HBV-related HCC.J Transl Med. 2019 Jan 3;17(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1761-7. J Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 30602391 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA Expression Profiles Identify Biomarker for Differentiating the Embolic Stroke from Thrombotic Stroke.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Dec 6;2018:4514178. doi: 10.1155/2018/4514178. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30627556 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of invasion-metastasis-associated microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma based on bioinformatic analysis and experimental validation.J Transl Med. 2018 Sep 29;16(1):266. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1639-8. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30268144 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and interaction analysis of key genes and microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma by bioinformatics analysis.World J Surg Oncol. 2017 Mar 16;15(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s12957-017-1127-2. World J Surg Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28302149 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of miR-302b-5p expression and molecular mechanism in hepatocellular carcinoma: Findings based on RT-qPCR and in silico analysis.Pathol Res Pract. 2019 Jul;215(7):152424. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2019.04.016. Epub 2019 Apr 29. Pathol Res Pract. 2019. PMID: 31103408
Cited by
-
Key events in cancer: Dysregulation of SREBPs.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 8;14:1130747. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1130747. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36969840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-29c inhibits HCV replication via activation of type I IFN response by targeting STAT3 in JFH-1-infected Huh7 cells.RSC Adv. 2018 Feb 20;8(15):8164-8172. doi: 10.1039/c7ra12815k. eCollection 2018 Feb 19. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35542013 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Networks for Cancer Candidate Biomarkers Discovery.Cancer Inform. 2016 Sep 4;15(Suppl 3):1-7. doi: 10.4137/CIN.S39458. eCollection 2016. Cancer Inform. 2016. PMID: 27625573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and functional activity of Nik related kinase (NRK) in benign hyperplastic prostate.J Transl Med. 2024 Mar 9;22(1):255. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05048-3. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38459501 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of MSMO1 promotes the development and progression of pancreatic cancer.J Cancer. 2022 Aug 1;13(10):3013-3021. doi: 10.7150/jca.73112. eCollection 2022. J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36046654 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bosetti C, Turati F, La Vecchia C. Hepatocellular carcinoma epidemiology. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2014;28(5):753–770. - PubMed
-
- Morgan RL, Baack B, Smith BD, Yartel A, Pitasi M, Falck-Ytter Y. Eradication of hepatitis C virus infection and the development of hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Ann Intern Med. 2013;158:329–337. - PubMed
-
- Singal A, Freeman D, Jr, Anand B. Meta-analysis: interferon improves outcomes following ablation or resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010;32:851–858. - PubMed
-
- Shalmani H, Ranjbar M, Alizadeh A. Recommendations for prevention and control of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection and HCV-related chronic disease. J Liver. 2013;3:2167–2889.
-
- Montalto G, Cervello M, Giannitrapani L, Dantona F, Terranova A, Castagnetta LA. Epidemiology, risk factors, and natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002;963:13–20. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

