Visual Plasticity: Blindsight Bridges Anatomy and Function in the Visual System
- PMID: 26811892
- PMCID: PMC5172419
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.11.026
Visual Plasticity: Blindsight Bridges Anatomy and Function in the Visual System
Abstract
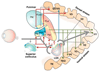
Some people who are blind due to damage to their primary visual cortex, V1, can discriminate stimuli presented within their blind visual field. This residual function has been recently linked to a pathway that bypasses V1, and connects the thalamic lateral geniculate nucleus directly with the extrastriate cortical area MT.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment on
-
Human blindsight is mediated by an intact geniculo-extrastriate pathway.Elife. 2015 Oct 20;4:e08935. doi: 10.7554/eLife.08935. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26485034 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fernel JF. De Naturali Parte Medicinae Libri Septem. Chapter 1. Paris: Simon de Colines; 1542.
-
- Riddoch G. Dissociation of visual perceptions due to occipital injuries, with especial reference to appreciation of movement. Brain. 1917;40:15–57.
-
- Weiskrantz L, Warrington EK, Sanders MD, Marshall J. Visual capacity in the hemianopic field following a restricted occipital ablation. Brain. 1974;97:709–728. - PubMed
-
- Leh SE, Johansen-Berg H, Ptito A. Unconscious vision: new insights into the neuronal correlate of blindsight using diffusion tractography. Brain. 2006;129:1822–1832. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

