Nanopore Sequencing as a Rapidly Deployable Ebola Outbreak Tool
- PMID: 26812583
- PMCID: PMC4734547
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2202.151796
Nanopore Sequencing as a Rapidly Deployable Ebola Outbreak Tool
Abstract
Rapid sequencing of RNA/DNA from pathogen samples obtained during disease outbreaks provides critical scientific and public health information. However, challenges exist for exporting samples to laboratories or establishing conventional sequencers in remote outbreak regions. We successfully used a novel, pocket-sized nanopore sequencer at a field diagnostic laboratory in Liberia during the current Ebola virus outbreak.
Keywords: DNA; Ebola hemorrhagic fever; Ebola virus; Ebola virus disease; Ebolavirus; Liberia; West Africa; disease outbreaks; high-throughput nucleotide sequencing; molecular diagnostic techniques; nanopore sequencing; viruses.
Figures
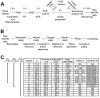
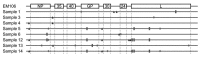
References
-
- Grolla A, Jones S, Kobinger G, Sprecher A, Girard G, Yao M, et al. Flexibility of mobile laboratory unit in support of patient management during the 2007 Ebola-Zaire outbreak in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Zoonoses Public Health. 2012;59(Suppl 2):151–7 . 10.1111/j.1863-2378.2012.01477.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Allaranga Y, Kone ML, Formenty P, Libama F, Boumandouki P, Woodfill CJ, et al. Lessons learned during active epidemiological surveillance of Ebola and Marburg viral hemorrhagic fever epidemics in Africa. East Afr J Public Health. 2010;7:30–6 . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

