Distinctive effects of CD34- and CD133-specific antibody-coated stents on re-endothelialization and in-stent restenosis at the early phase of vascular injury
- PMID: 26813006
- PMCID: PMC4669017
- DOI: 10.1093/rb/rbv007
Distinctive effects of CD34- and CD133-specific antibody-coated stents on re-endothelialization and in-stent restenosis at the early phase of vascular injury
Abstract
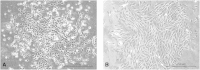
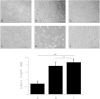
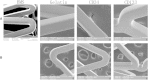
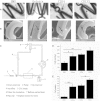
It is not clear what effects of CD34- and CD133-specific antibody-coated stents have on re-endothelialization and in-stent restenosis (ISR) at the early phase of vascular injury. This study aims at determining the capabilities of different coatings on stents (e.g. gelatin, anti-CD133 and anti-CD34 antibodies) to promote adhesion and proliferation of endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs). The in vitro study revealed that the adhesion force enabled the EPCs coated on glass slides to withstand flow-induced shear stress, so that allowing for the growth of the cells on the slides for 48 h. The in vivo experiment using a rabbit model in which the coated stents with different substrates were implanted showed that anti-CD34 and anti-CD133 antibody-coated stents markedly reduced the intima area and restenosis than bare mental stents (BMS) and gelatin-coated stents. Compared with the anti-CD34 antibody-coated stents, the time of cells adhesion was longer and earlier present in the anti-CD133 antibody-coated stents and anti-CD133 antibody-coated stents have superiority in re-endothelialization and inhibition of ISR. In conclusion, this study demonstrated that anti-CD133 antibody as a stent coating for capturing EPCs is better than anti-CD34 antibody in promoting endothelialization and reducing ISR.
Keywords: CD133; CD34; endothelial progenitor cells; re-endothelialization; stent.
Figures


Similar articles
-
First in vitro and in vivo results of an anti-human CD133-antibody coated coronary stent in the porcine model.Clin Res Cardiol. 2013 Jun;102(6):413-25. doi: 10.1007/s00392-013-0547-4. Epub 2013 Feb 10. Clin Res Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23397592
-
In situ endothelialization of intravascular stents coated with an anti-CD34 antibody functionalized heparin-collagen multilayer.Biomaterials. 2010 May;31(14):4017-25. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.01.092. Epub 2010 Feb 9. Biomaterials. 2010. PMID: 20149438
-
Study of a novel coating strategy for coronary stents: evaluation of stainless metallic steel coated with VEGF and anti-CD34 antibody in vitro.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016;20(2):311-6. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26875902
-
Progress and prospects of endothelial progenitor cell therapy in coronary stent implantation.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2016 Aug;104(6):1237-47. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.33398. Epub 2015 Jun 7. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2016. PMID: 26059710 Review.
-
Ex vivo and preclinical assessment of an endothelial progenitor cell capturing bioengineered stent.Minerva Cardioangiol. 2012 Feb;60(1):11-21. Minerva Cardioangiol. 2012. PMID: 22322570 Review.
Cited by
-
Laser Additive Manufacturing of Anti-Tetrachiral Endovascular Stents with Negative Poisson's Ratio and Favorable Cytocompatibility.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Jul 18;13(7):1135. doi: 10.3390/mi13071135. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35888952 Free PMC article.
-
A Recombinant Fusion Construct between Human Serum Albumin and NTPDase CD39 Allows Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Thrombotic Coating of Medical Devices.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Sep 18;13(9):1504. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13091504. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34575580 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies to develop endogenous stem cell-recruiting bioactive materials for tissue repair and regeneration.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017 Oct 1;120:50-70. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2017.07.011. Epub 2017 Jul 19. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017. PMID: 28734899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Endothelial injury and its repair strategies after intravascular stents implantation].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2018 Apr 25;35(2):307-313. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.201612008. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29745539 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Recent advances in surface functionalization of cardiovascular stents.Bioact Mater. 2024 Oct 28;44:389-410. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.10.025. eCollection 2025 Feb. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 39539518 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Holmes DRJ, Vlietstra RE, Smith HC, et al. Restenosis after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA): a report from the PTCA Registry of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Am J Cardiol 1984;53:C77–81. - PubMed
-
- Morice MC, Serruys PW, Sousa JE, et al. A randomized comparison of a sirolimus-eluting stent with a standard stent for coronary revascularization. N Engl J Med 2002;346:1773–80. - PubMed
-
- Stone GW, Ellis SG, Cox DA, et al. A polymer-based, paclitaxel-eluting stent in patients with coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 2004;350:221–31. - PubMed
-
- Garg P, Normand SL, Silbaugh TS, et al. Drug-eluting or bare-metal stenting in patients with diabetes mellitus: results from the Massachusetts Data Analysis Center Registry. Circulation 2008;118:2277–85. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

