Interactions of C4 Subtype Metabolic Activities and Transport in Maize Are Revealed through the Characterization of DCT2 Mutants
- PMID: 26813621
- PMCID: PMC4790864
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.15.00497
Interactions of C4 Subtype Metabolic Activities and Transport in Maize Are Revealed through the Characterization of DCT2 Mutants
Abstract
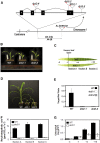
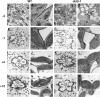
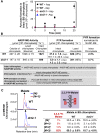
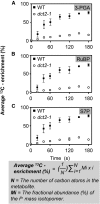
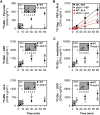
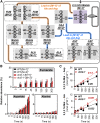
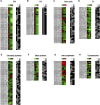
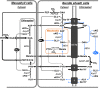
C4 photosynthesis in grasses requires the coordinated movement of metabolites through two specialized leaf cell types, mesophyll (M) and bundle sheath (BS), to concentrate CO2 around Rubisco. Despite the importance of transporters in this process, few have been identified or rigorously characterized. In maize (Zea mays), DCT2 has been proposed to function as a plastid-localized malate transporter and is preferentially expressed in BS cells. Here, we characterized the role of DCT2 in maize leaves using Activator-tagged mutant alleles. Our results indicate that DCT2 enables the transport of malate into the BS chloroplast. Isotopic labeling experiments show that the loss of DCT2 results in markedly different metabolic network operation and dramatically reduced biomass production. In the absence of a functioning malate shuttle, dct2 lines survive through the enhanced use of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase carbon shuttle pathway that in wild-type maize accounts for ∼ 25% of the photosynthetic activity. The results emphasize the importance of malate transport during C4 photosynthesis, define the role of a primary malate transporter in BS cells, and support a model for carbon exchange between BS and M cells in maize.
© 2016 American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Becker T.W., Carrayol E., Hirel B. (2000). Glutamine synthetase and glutamate dehydrogenase isoforms in maize leaves: localization, relative proportion and their role in ammonium assimilation or nitrogen transport. Planta 211: 800–806. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

