Lean body mass as an independent determinant of dose-limiting toxicity and neuropathy in patients with colon cancer treated with FOLFOX regimens
- PMID: 26814378
- PMCID: PMC4831278
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.621
Lean body mass as an independent determinant of dose-limiting toxicity and neuropathy in patients with colon cancer treated with FOLFOX regimens
Abstract
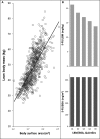
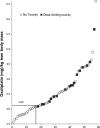
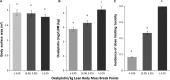
Evidence suggests that lean body mass (LBM) may be useful to normalize chemotherapy doses. Data from one prospective and one retrospective study were used to determine if the highest doses of oxaliplatin/kg LBM within FOLFOX regimens would be associated with dose-limiting toxicity (DLT) in colon cancer patients. Toxicity over four cycles was graded according to NCI Common Toxicity Criteria V2 or V3 (Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, MD). Muscle tissue was measured by computerized tomography (CT) and used to evaluate the LBM compartment of the whole body. In prospective randomized clinical trials conducted in France (n = 58), for patients given FOLFOX-based regimens according to body surface area, values of oxaliplatin/kg LBM were highly variable, ranging from 2.55 to 6.6 mg/kg LBM. A cut point of 3.09 mg oxaliplatin/kg LBM for developing toxicity was determined by Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) analysis, below this value 0/17 (0.0%) of patients experienced DLT; in contrast above this value 18/41 (44.0%) of patients were dose reduced or had treatment terminated owing to toxicity (≥Grade 3 or neuropathy ≥Grade 2); for 9/41 the DLT was sensory neuropathy. These findings were validated in an independent cohort of colon cancer patients (n = 80) receiving FOLFOX regimens as part of standard care, in Canada. Low LBM is a significant predictor of toxicity and neuropathy in patients administered FOLFOX-based regimens using conventional body surface area (BSA) dosing.
Keywords: Body composition; chemotherapy toxicity; colon cancer; irinotecan; lean body mass; neuropathy; oxaliplatin.
© 2016 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Sawyer, M. , and Ratain M. J.. 2001. Body surface area as a determinant of pharmacokinetics and drug dosing. Invest. New Drugs 19:171–177. - PubMed
-
- Morgan, D. J. , and Bray K. M.. 1994. Lean body mass as a predictor of drug dosage. Implications for drug therapy. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 26:292–307. - PubMed
-
- Aslani, A. , Smith R. C., Allen B. J., Pavlakis N., and Levi J. A.. 2000. The predictive value of body protein for chemotherapy‐induced toxicity. Cancer 88:796–803. - PubMed
-
- Ratain, M. J. 1998. Body surface area as a basis for dosing of anticancer agents: science, myth or habit? J. Clin. Oncol. 16:2297–2298. - PubMed
-
- Baker, S. D. , Grochow L. B., and Donehower R. C.. 1995. Should anticancer drug doses be adjusted in the obese patient? J. Natl Cancer Inst. 87:333–334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

