Remodeling myelination: implications for mechanisms of neural plasticity
- PMID: 26814588
- PMCID: PMC4792270
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.4200
Remodeling myelination: implications for mechanisms of neural plasticity
Abstract
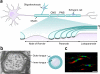
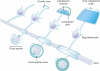
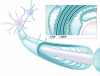
One of the most significant paradigm shifts in membrane remodeling is the emerging view that membrane transformation is not exclusively controlled by cytoskeletal rearrangement, but also by biophysical constraints, adhesive forces, membrane curvature and compaction. One of the most exquisite examples of membrane remodeling is myelination. The advent of myelin was instrumental in advancing the nervous system during vertebrate evolution. With more rapid and efficient communication between neurons, faster and more complex computations could be performed in a given time and space. Our knowledge of how myelin-forming oligodendrocytes select and wrap axons has been limited by insufficient spatial and temporal resolution. By virtue of recent technological advances, progress has clarified longstanding controversies in the field. Here we review insights into myelination, from target selection to axon wrapping and membrane compaction, and discuss how understanding these processes has unexpectedly opened new avenues of insight into myelination-centered mechanisms of neural plasticity.
Figures
References
-
- Hartline DK, Colman DR. Rapid conduction and the evolution of giant axons and myelinated fibers. Curr. Biol. 2007;17:R29–R35. - PubMed
-
- Zalc B, Goujet D, Colman D. The origin of the myelination program in vertebrates. Curr. Biol. 2008;18:R511–R512. - PubMed
-
- Ben Geren B. The formation from the Schwann cell surface of myelin in the peripheral nerves of chick embryos. Exp. Cell Res. 1954;7:558–562. - PubMed
-
- Bunge MB, Bunge RP, Pappas GD. Electron microscopic demonstration of connections between glia and myelin sheaths in the developing mammalian central nervous system. J. Cell Biol. 1962;12:448–453. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- CA125123/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HD007495/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD007495/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS062796/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS095889/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD007495/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA125123/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056338/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK56338/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F31 NS081905/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS062796/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F31NS081905/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD007495/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

