Dynamic Regulation of AMPAR Phosphorylation In Vivo Following Acute Behavioral Stress
- PMID: 26814839
- PMCID: PMC11482403
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-016-0332-9
Dynamic Regulation of AMPAR Phosphorylation In Vivo Following Acute Behavioral Stress
Abstract
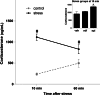
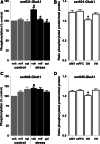
The tuning of glutamatergic transmission is an essential mechanism for neuronal communication. α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors (AMPARs) are ionotropic glutamate receptors that mediate fast synaptic transmission. The phosphorylation states of specific serine residues on the GluA1 and GluA2 AMPAR subunits are considered critical post-translational modifications that regulate AMPAR activity and subcellular trafficking. While behavioral stress, via stress hormones, exerts specific alterations on such glutamatergic processes, there have been conflicting data concerning the influence of stress on AMPAR phosphorylation in different brain regions, and the post-stress signaling mechanisms mediating these processes are not well delineated. Here, we examined the dynamics of phosphorylation at three AMPAR serine residues (ser831-GluA1, ser845-GluA1, and ser880-GluA2) in four brain regions [amygdala, medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), dorsal hippocampus, and ventral hippocampus] of the rat during the hour following behavioral stress. We also tested the impact of post-stress corticosteroid receptor blockade on AMPAR phosphorylation. Both GluA1 subunit residues exhibited elevated phosphorylation after stress, yet post-stress administration of corticosteroid receptor antagonists curtailed these effects only at ser831-GluA1. In contrast, ser880-GluA2 displayed a time-dependent tendency for early decreased phosphorylation (that was selectively augmented by mifepristone treatment in the amygdala and mPFC of stressed animals) followed by increased phosphorylation later on. These findings show that the in vivo regulation of AMPAR phosphorylation after stress is a dynamic and subunit-specific process, and they provide support for the hypothesis that corticosteroid receptors have an ongoing role in the regulation of ser831-GluA1 phosphorylation during the post-stress interval.
Keywords: AMPA; Amygdala; Phosphorylation; Prefrontal cortex; Spironolactone; Stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Acute stress induces contrasting changes in AMPA receptor subunit phosphorylation within the prefrontal cortex, amygdala and hippocampus.PLoS One. 2010 Dec 8;5(12):e15282. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015282. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21170339 Free PMC article.
-
ABA renewal involves enhancements in both GluA2-lacking AMPA receptor activity and GluA1 phosphorylation in the lateral amygdala.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 12;9(6):e100108. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100108. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24925360 Free PMC article.
-
Sexually dimorphic long-term effects of an early life experience on AMPA receptor subunit expression in rat brain.Neuroscience. 2014 Jan 17;257:49-64. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.10.073. Epub 2013 Nov 8. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24211798
-
Identification of new phosphorylation sites of AMPA receptors in the rat hippocampus--A resource for neuroscience research.Proteomics Clin Appl. 2015 Oct;9(9-10):808-16. doi: 10.1002/prca.201400057. Epub 2015 May 15. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2015. PMID: 25656447 Review.
-
A Scoping Review of Corticosterone-Induced Changes in Ionotropic Glutamate Receptor Levels and Localization in the Rodent Brain: Implications for the Auditory System.Brain Sci. 2025 Jan 24;15(2):110. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15020110. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 40002443 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acute Neuroinflammation Promotes Cell Responses to 1800 MHz GSM Electromagnetic Fields in the Rat Cerebral Cortex.Neurotox Res. 2017 Oct;32(3):444-459. doi: 10.1007/s12640-017-9756-3. Epub 2017 Jun 3. Neurotox Res. 2017. PMID: 28578480
-
A single high dose of dexamethasone affects the phosphorylation state of glutamate AMPA receptors in the human limbic system.Transl Psychiatry. 2016 Dec 13;6(12):e986. doi: 10.1038/tp.2016.251. Transl Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27959333 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Chronic Intermittent Ethanol Exposure Selectively Increases Synaptic Excitability in the Ventral Domain of the Rat Hippocampus.Neuroscience. 2019 Feb 1;398:144-157. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.11.028. Epub 2018 Nov 24. Neuroscience. 2019. PMID: 30481568 Free PMC article.
-
AMPA and NMDA Receptors in Hippocampus of Rats with Fluoride-Induced Cognitive Decline.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 2;25(21):11796. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111796. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39519348 Free PMC article.
-
Neurobiology of Depression: Chronic Stress Alters the Glutamatergic System in the Brain-Focusing on AMPA Receptor.Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 27;10(5):1005. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10051005. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35625742 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abraham WC (2008) Metaplasticity: tuning synapses and networks for plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci 9(5):387 - PubMed
-
- Alzamora R, Harvey BJ (2008) Direct binding and activation of protein kinase C isoforms by steroid hormones. Steroids 73(9):885–888 - PubMed
-
- Birnbaum SG, Yuan P, Wang M, Vijayraghavan S, Bloom A, Davis D, Gobeske K, Sweatt J, Manji H, Arnsten A (2004) Protein kinase C overactivity impairs prefrontal cortical regulation of working memory. Science 306(5697):882–884 - PubMed
-
- Brewin CR, Andrews B, Valentine JD (2000) Meta-analysis of risk factors for posttraumatic stress disorder in trauma-exposed adults. J Consult Clin Psychol 68(5):748–766 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

