Can the Direct Medical Cost of Chronic Disease Be Transferred across Different Countries? Using Cost-of-Illness Studies on Type 2 Diabetes, Epilepsy and Schizophrenia as Examples
- PMID: 26814959
- PMCID: PMC4731392
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147169
Can the Direct Medical Cost of Chronic Disease Be Transferred across Different Countries? Using Cost-of-Illness Studies on Type 2 Diabetes, Epilepsy and Schizophrenia as Examples
Abstract
Objectives: To systematically review cost of illness studies for schizophrenia (SC), epilepsy (EP) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and explore the transferability of direct medical cost across countries.
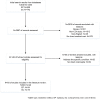
Methods: A comprehensive literature search was performed to yield studies that estimated direct medical costs. A generalized linear model (GLM) with gamma distribution and log link was utilized to explore the variation in costs that accounted by the included factors. Both parametric (Random-effects model) and non-parametric (Boot-strapping) meta-analyses were performed to pool the converted raw cost data (expressed as percentage of GDP/capita of the country where the study was conducted).
Results: In total, 93 articles were included (40 studies were for T2DM, 34 studies for EP and 19 studies for SC). Significant variances were detected inter- and intra-disease classes for the direct medical costs. Multivariate analysis identified that GDP/capita (p<0.05) was a significant factor contributing to the large variance in the cost results. Bootstrapping meta-analysis generated more conservative estimations with slightly wider 95% confidence intervals (CI) than the parametric meta-analysis, yielding a mean (95%CI) of 16.43% (11.32, 21.54) for T2DM, 36.17% (22.34, 50.00) for SC and 10.49% (7.86, 13.41) for EP.
Conclusions: Converting the raw cost data into percentage of GDP/capita of individual country was demonstrated to be a feasible approach to transfer the direct medical cost across countries. The approach from our study to obtain an estimated direct cost value along with the size of specific disease population from each jurisdiction could be used for a quick check on the economic burden of particular disease for countries without such data.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Estimating the costs of epilepsy: an international comparison of epilepsy cost studies.Epilepsia. 2001 May;42(5):634-40. doi: 10.1046/j.1528-1157.2001.18200.x. Epilepsia. 2001. PMID: 11380571 Review.
-
The cost of schizophrenia: lessons from an international comparison.J Ment Health Policy Econ. 2006 Dec;9(4):177-83. J Ment Health Policy Econ. 2006. PMID: 17200594
-
A comparison of methods to handle skew distributed cost variables in the analysis of the resource consumption in schizophrenia treatment.J Ment Health Policy Econ. 2002 Mar;5(1):21-31. J Ment Health Policy Econ. 2002. PMID: 12529567
-
[The cost of schizophrenia: a literature review].Encephale. 2013 May;39 Suppl 1:S49-56. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2012.11.004. Epub 2013 Jan 23. Encephale. 2013. PMID: 23351935 Review. French.
-
Direct medical costs for complications among children and adults with diabetes in the US commercial payer setting.Appl Health Econ Health Policy. 2014 Apr;12(2):219-30. doi: 10.1007/s40258-014-0086-9. Appl Health Econ Health Policy. 2014. PMID: 24573912
Cited by
-
How Cost-of-Illness (COI) Study Provides Direct and Indirect Costs of Multiple Sclerosis (MS) in Bosnia and Herzegovina ?Mater Sociomed. 2018 Dec;30(4):270-275. doi: 10.5455/msm.2018.30.270-275. Mater Sociomed. 2018. PMID: 30936791 Free PMC article.
-
Early specialized care after a first unprovoked epileptic seizure.J Neurol. 2016 Dec;263(12):2386-2394. doi: 10.1007/s00415-016-8272-3. Epub 2016 Sep 7. J Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27604619 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparing Medical Training Costs Internationally: A Systematic Review.Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2024 Apr 17;38:43. doi: 10.47176/mjiri.38.43. eCollection 2024. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2024. PMID: 39399605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cost-of-illness studies in nine Central and Eastern European countries.Eur J Health Econ. 2019 Jun;20(Suppl 1):155-172. doi: 10.1007/s10198-019-01066-x. Epub 2019 May 18. Eur J Health Econ. 2019. PMID: 31104219 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of H2H management mode on blood sugar control and living ability in patients with schizophrenia and type 2 diabetes mellitus.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Jan 15;15(1):223-232. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 36777852 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhao FL, Xie F, Hu H, Li SC. Transferability of Indirect Cost of Chronic Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmacoeconomics. 2013;26:26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical