Association between Functional Variables and Heart Failure after Myocardial Infarction in Rats
- PMID: 26815462
- PMCID: PMC4765008
- DOI: 10.5935/abc.20160015
Association between Functional Variables and Heart Failure after Myocardial Infarction in Rats
Erratum in
-
Erratum.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2016 Mar;106(3):267. doi: 10.5935/abc.20160034. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27027373 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Heart failure prediction after acute myocardial infarction may have important clinical implications.
Objective: To analyze the functional echocardiographic variables associated with heart failure in an infarction model in rats.
Methods: The animals were divided into two groups: control and infarction. Subsequently, the infarcted animals were divided into groups: with and without heart failure. The predictive values were assessed by logistic regression. The cutoff values predictive of heart failure were determined using ROC curves.
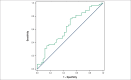
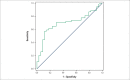
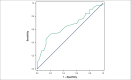
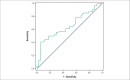
Results: Six months after surgery, 88 infarcted animals and 43 control animals were included in the study. Myocardial infarction increased left cavity diameters and the mass and wall thickness of the left ventricle. Additionally, myocardial infarction resulted in systolic and diastolic dysfunction, characterized by lower area variation fraction values, posterior wall shortening velocity, E-wave deceleration time, associated with higher values of E / A ratio and isovolumic relaxation time adjusted by heart rate. Among the infarcted animals, 54 (61%) developed heart failure. Rats with heart failure have higher left cavity mass index and diameter, associated with worsening of functional variables. The area variation fraction, the E/A ratio, E-wave deceleration time and isovolumic relaxation time adjusted by heart rate were functional variables predictors of heart failure. The cutoff values of functional variables associated with heart failure were: area variation fraction < 31.18%; E / A > 3.077; E-wave deceleration time < 42.11 and isovolumic relaxation time adjusted by heart rate < 69.08.
Conclusion: In rats followed for 6 months after myocardial infarction, the area variation fraction, E/A ratio, E-wave deceleration time and isovolumic relaxation time adjusted by heart rate are predictors of heart failure onset.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical aspects of left ventricular diastolic function assessed by Doppler echocardiography following acute myocardial infarction.Dan Med Bull. 2001 Nov;48(4):199-210. Dan Med Bull. 2001. PMID: 11767125 Review.
-
Relationship between echocardiographic parameters and exercise test duration in patients after myocardial infarction.Cardiol J. 2009;16(6):507-13. Cardiol J. 2009. PMID: 19950086
-
Heart failure after myocardial infarction: the importance of diastolic dysfunction. A prospective clinical and echocardiographic study.Eur Heart J. 1995 Apr;16(4):496-505. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a060942. Eur Heart J. 1995. PMID: 7671895
-
[Evaluation of myocardial systolic function of heart failure induced by myocardial infarction in rats with strain and strain rate imagine].Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2010 Jun;35(6):590-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7347.2010.06.009. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2010. PMID: 20622332 Chinese.
-
Left ventricular systolic function after acute myocardial infarction: prognostic importance, relation to congestive heart failure and as a target for intervention.Dan Med Bull. 1999 Jun;46(3):235-48. Dan Med Bull. 1999. PMID: 10421980 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Rosemary supplementation (Rosmarinus oficinallis L.) attenuates cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction in rats.PLoS One. 2017 May 11;12(5):e0177521. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177521. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28494028 Free PMC article.
-
Hypercaloric diet models do not develop heart failure, but the excess sucrose promotes contractility dysfunction.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 7;15(2):e0228860. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228860. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32032383 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-132 attenuated cardiac fibrosis in myocardial infarction-induced heart failure rats.Biosci Rep. 2020 Sep 30;40(9):BSR20201696. doi: 10.1042/BSR20201696. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32885809 Free PMC article.
-
MircroRNA-145 Attenuates Cardiac Fibrosis Via Regulating Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase Kinase 3.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2023 Aug;37(4):655-665. doi: 10.1007/s10557-021-07312-w. Epub 2022 Apr 13. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2023. PMID: 35416554
References
-
- Liu L, Eisen HJ. Epidemiology of heart failure and scope of the problem. Cardiol Clin. 2014;32(1):1–8. - PubMed
-
- Zornoff LA, Paiva SA, Minicucci MF, Spadaro J. Experimental myocardium infarction in rats: analysis of the model. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2009;93(4):434-40, 426-32. - PubMed
-
- Martinez PF, Okoshi K, Zornoff LA, Oliveira SA, Jr, Campos DH, Lima AR, et al. Echocardiographic detection of congestive heart failure in postinfarction rats. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2011;111(2):543–551. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

