The Coagulation Factor XIIa Inhibitor rHA-Infestin-4 Improves Outcome after Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rats
- PMID: 26815580
- PMCID: PMC4731395
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146783
The Coagulation Factor XIIa Inhibitor rHA-Infestin-4 Improves Outcome after Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rats
Abstract
Background and purpose: Ischemic stroke provokes severe brain damage and remains a predominant disease in industrialized countries. The coagulation factor XII (FXII)-driven contact activation system plays a central, but not yet fully defined pathogenic role in stroke development. Here, we investigated the efficacy of the FXIIa inhibitor rHA-Infestin-4 in a rat model of ischemic stroke using both a prophylactic and a therapeutic approach.
Methods: For prophylactic treatment, animals were treated intravenously with 100 mg/kg rHA-Infestin-4 or an equal volume of saline 15 min prior to transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO) of 90 min. For therapeutic treatment, 100 mg/kg rHA-Infestin-4, or an equal volume of saline, was administered directly after the start of reperfusion. At 24 h after tMCAO, rats were tested for neurological deficits and blood was drawn for coagulation assays. Finally, brains were removed and analyzed for infarct area and edema formation.
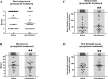
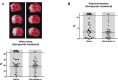
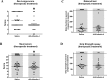
Results: Within prophylactic rHA-Infestin-4 treatment, infarct areas and brain edema formation were reduced accompanied by better neurological scores and survival compared to controls. Following therapeutic treatment, neurological outcome and survival were still improved although overall effects were less pronounced compared to prophylaxis.
Conclusions: With regard to the central role of the FXII-driven contact activation system in ischemic stroke, inhibition of FXIIa may represent a new and promising treatment approach to prevent cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

