Geriatric forensics - Part 2 "Prevalence of elder abuse and their potential forensic markers among medical and dental patients"
- PMID: 26816460
- PMCID: PMC4714408
- DOI: 10.4103/0975-1475.172436
Geriatric forensics - Part 2 "Prevalence of elder abuse and their potential forensic markers among medical and dental patients"
Abstract
Context: This study is a continuation of the earlier studies and has been extended to investigate the potential forensic markers of elder abuse.
Aims: To determine the prevalence of elder abuse in various outpatient departments (OPDs). To study the associated parameters related to the abuser and the abused. To determine the existence of potential forensic markers of elder abuse.
Settings and design: The subjects were randomly selected from the medical and the dental OPDs of the university.
Materials and methods: Eight hundred and thirty two elderly subjects in the age range 40-60 years were interviewed using a questionnaire to determine the existence of elder abuse. The subjects were investigated and examined for weight, nutrition and hydration, vital signs, habits, existing visual and auditory capabilities, medications, disclosure of wills/deeds, signs of depression, and documented cleanliness. The mini-mental state examination, the Geriatric Depression Scale, the Clock drawing test, and the Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale were used to determine the potential forensic markers.
Statistical analysis used: Mean values in percentage were determined by dividing the number of determined subjects by the total number of subjects for that parameter.
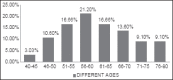
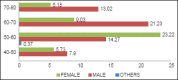
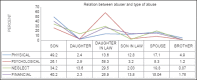
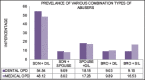
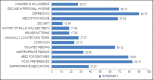
Results: About 37% in medical and 41% in dental OPDs were found to have suffered from abuse, mostly in the age group 60-70 years. Females received more abuse and a combination of son and daughter-in-law constituted most abusers. Various potential markers of elder abuse and neglect investigated among the elder abuse victims included depression (89%), signs of improper feeding (83%), changes in personal hygiene (69%), need for medical/dental treatment (78%), medication misuse (67%), changes in wills/deeds (26%), decubiti (10%), bruises (17%), skin tears (27%), and confusion (23%).
Conclusions: Elder abuse exists in one or more forms in both medical and dental OPDs among both males and females in all age groups.
Keywords: Deed; depression; domestic violence; neglect; personal hygiene.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Geriatric forensics: A dentist's perspective and contribution to identify existence of elder abuse among his patients.J Forensic Dent Sci. 2010 Jul;2(2):81-5. doi: 10.4103/0975-1475.81287. J Forensic Dent Sci. 2010. PMID: 21731345 Free PMC article.
-
Recognition and perception of elder abuse by prehospital and hospital-based care providers.Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2009 Jan-Feb;48(1):110-5. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2007.11.002. Epub 2007 Dec 26. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2009. PMID: 18160115
-
Extent of Elder Abuse Training in Dental Hygiene Curricula and Program Directors' Perceptions of Importance of and Barriers to Implementation.J Dent Educ. 2019 Jan;83(1):39-47. doi: 10.21815/JDE.019.005. J Dent Educ. 2019. PMID: 30600248
-
Recommendations for the elder abuse, health, and justice fields about medical forensic issues related to elder abuse and neglect.J Elder Abuse Negl. 2006;18(4):suppl 41-81. J Elder Abuse Negl. 2006. PMID: 17972663 Review.
-
Neglect of Older People: Touching on Forensic and Pathophysiological Aspects.Gerontologist. 2020 Aug 14;60(6):e449-e465. doi: 10.1093/geront/gnz084. Gerontologist. 2020. PMID: 31348828 Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of dentistry in identifying and supporting individuals who have experienced gender-based violence: a scoping review.BMJ Public Health. 2025 May 26;3(1):e001770. doi: 10.1136/bmjph-2024-001770. eCollection 2025. BMJ Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40433069 Free PMC article.
-
Elder abuse without borders: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Public Health. 2025 Jul 2;25(1):2268. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-23548-9. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40604591 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Sensitization of Family Caregivers upon Treatment Compliance among Geriatric Patients Suffering from Elder Abuse and Neglect.Healthcare (Basel). 2021 Feb 18;9(2):226. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9020226. Healthcare (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33670706 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitizing Family Caregivers to Influence Treatment Compliance among Elderly Neglected Patients-A 2-Year Longitudinal Study Outcome in Completely Edentulous Patients.Healthcare (Basel). 2021 May 2;9(5):533. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9050533. Healthcare (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34063316 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Drunkard son kills father. The Times of India. 2011. Oct, [Last accessed on 2011 Oct 11]. Available from: http://www.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/drunkard-son-killsfather/ar... .
-
- Drunkard son kills father in Uttar Pradesh. [Last accessed on 2012 Jun 09]. Available from: http://www.ibnlive.in.com/news/drunkard- son-kills-father-in-uttar- prad... .
-
- Horrifying case of son killed his father rocked the Rae bareli. [Last accessed on 2013 May 07]. Available from: http://www.dailypioneer.com/state-editions/lucknow/horrifying-case-of-so... .
-
- Sons hire contract killer for murdering 70-year-old father. [Last accessed on 2014 Mar 03]. Available from: http://www.news18.com/news/uttar-pradesh/sons-hire-contract-killer-for-m... .
-
- Man kills father, step-brother, wife over property dispute. The Times of India. [Last accessed on 2014 Mar 07]. Available from: http://www.article.wn.com/view/2013/12/30/Man_kills_father_stepbrother_w...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
