Non-melanoma skin cancer treated with high-dose-rate brachytherapy and Valencia applicator in elderly patients: a retrospective case series
- PMID: 26816500
- PMCID: PMC4716125
- DOI: 10.5114/jcb.2015.55746
Non-melanoma skin cancer treated with high-dose-rate brachytherapy and Valencia applicator in elderly patients: a retrospective case series
Abstract
Purpose: The incidence of non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC) has been increasing over the past 30 years. Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the two most common subtypes of NMSC. The aim of this study was to estimate tumour control, toxicity, and aesthetic events in elderly patients treated with high-dose-rate (HDR) brachytherapy (BT) using Valencia applicator.
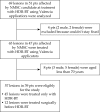
Material and methods: From January 2012 to May 2015, 57 lesions in 39 elderly eligible patients were enrolled. All the lesions had a diameter ≤ 25 mm (median: 12.5 mm) and a depth ≤ 4 mm. The appropriate Valencia applicator, 2 or 3 cm in diameter was used. The prescribed dose was 40 Gy in 8 fractions (5 Gy/fraction) in 48 lesions (group A), and 50 Gy in 10 fractions (5 Gy/fraction) in 9 lesions (group B), delivered 2/3 times a week. The biological effective dose (BED) was 60 Gy and 75 Gy, respectively.
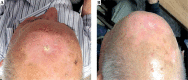
Results: After median follow-up of 12 months, 96.25% lesions showed a complete response and only two cases presented partial remission. Radiation Therapy Oncology Group - European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (RTOG/EORTC) G 1-2 acute toxicities were observed in 63.2% of the lesions: 56.3% in group A and 77.7% in group B. Late G1-G2 toxicities was observed in 19.3% of the lesions: 18.8% in group A and 22.2% in group B, respectively. No G3 or higher acute or late toxicities occurred. In 86% of the lesions, an excellent cosmetic result was observed (87.5% in group A and 77.8% in group B). Six lesions had a good cosmetic outcome and only 2.3% presented a fair cosmetic impact.
Conclusions: The treatment of NMSC with HDR-BT using Valencia surface applicator is effective with excellent and good cosmetics results in elderly patients. The hypofractionated course appears effective and no statistical differences were observed between the two groups analysed.
Keywords: HDR brachytherapy; Valencia applicator; skin brachytherapy; skin cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Two different sizes of Valencia applicators in non-melanoma skin cancer treatment with iridium-192 high-dose-rate brachytherapy.J Contemp Brachytherapy. 2021 Dec;13(6):615-619. doi: 10.5114/jcb.2021.112111. Epub 2021 Dec 30. J Contemp Brachytherapy. 2021. PMID: 35079246 Free PMC article.
-
Non-melanoma skin cancer treated with HDR Valencia applicator: clinical outcomes.J Contemp Brachytherapy. 2014 Jun;6(2):167-72. doi: 10.5114/jcb.2014.43247. Epub 2014 Jun 3. J Contemp Brachytherapy. 2014. PMID: 25097557 Free PMC article.
-
High-dose-rate brachytherapy for non-melanoma skin cancer using tailored custom moulds - a single-centre experience.Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2021;25(1):12-16. doi: 10.5114/wo.2021.104688. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2021. PMID: 33911976 Free PMC article.
-
Non-melanoma skin cancer treated with high-dose-rate brachytherapy: a review of literature.J Contemp Brachytherapy. 2016 Dec;8(6):533-540. doi: 10.5114/jcb.2016.64112. Epub 2016 Dec 2. J Contemp Brachytherapy. 2016. PMID: 28115960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Elekta Esteya® electronic brachytherapy system in non-melanoma skin cancers: A post-market observational study.J Contemp Brachytherapy. 2024 Dec;16(6):478-488. doi: 10.5114/jcb.2024.146795. Epub 2024 Dec 31. J Contemp Brachytherapy. 2024. PMID: 39943976 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extensive Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma of the Feet Treated with High-Dose-Rate Brachytherapy and External Beam Radiation.Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2018 Aug 7;2018:5610925. doi: 10.1155/2018/5610925. eCollection 2018. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2018. PMID: 30174962 Free PMC article.
-
Individualized 3D scanning and printing for non-melanoma skin cancer brachytherapy: a financial study for its integration into clinical workflow.J Contemp Brachytherapy. 2017 Jun;9(3):270-276. doi: 10.5114/jcb.2017.68134. Epub 2017 May 30. J Contemp Brachytherapy. 2017. PMID: 28725252 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Melanoma Skin Cancers in the Older Patient.Curr Oncol Rep. 2019 Jul 29;21(9):79. doi: 10.1007/s11912-019-0828-9. Curr Oncol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31359294 Review.
-
Mould-based surface high-dose-rate brachytherapy for eyelid carcinoma.J Contemp Brachytherapy. 2019 Oct;11(5):443-448. doi: 10.5114/jcb.2019.88619. Epub 2019 Oct 30. J Contemp Brachytherapy. 2019. PMID: 31749853 Free PMC article.
-
Skin CanceR Brachytherapy vs External beam radiation therapy (SCRiBE) meta-analysis.Radiother Oncol. 2018 Mar;126(3):386-393. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2017.12.029. Epub 2018 Jan 19. Radiother Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29370985 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lomas A, Leonardi-Bee J, Bath-Hextall F. A systematic review of worldwide incidence of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:1069–1080. - PubMed
-
- Eisemann N, Waldmann A, Geller AC, et al. Non-melanoma skin cancer incidence and impact of skin cancer screening on incidence. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:43–50. - PubMed
-
- Kricker A, Armstrong BK, English DR, et al. Does intermittent sun exposure cause basal cell carcinoma. A case-control study in Western Australia. Int J Cancer. 1995;60:489–494. - PubMed
-
- Katalinic A, Kunze U, Schafer T. Epidemiology of cutaneous melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany: incidence, clinical subtypes, tumour stages and localization (epidemiology of skin cancer) Br J Dermatol. 2003;149:1200–1206. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous