Rad51 in regulating the radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer with different epidermal growth factor receptor mutation status
- PMID: 26816539
- PMCID: PMC4718133
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.12274
Rad51 in regulating the radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer with different epidermal growth factor receptor mutation status
Abstract
Background: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring kinase-domain mutations in epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR) has been observed to be sensitive to ionizing radiation (IR). We explore Rad51-dependent homologous recombination (HR) DNA repair in regulating radiosensitivity in two NSCLC cell lines with different EGFR mutation status.
Methods: NSCLC cell lines, wild-type EGFR A549 and mutant EGFR H820 with an in-frame deletion in exon 19 of EGFR (ΔE746-E750), were cultured. Radiosensitivity was estimated by colony forming assay. Rad51 expression was evaluated by quantitative real time-polymerase chain reaction and Western-blot. Lentiviral small hairpin ribonucleic acid-Rad51 and ΔE746-E750 deletion mutant EGFR were constructed and transfected into cells. Flowcytometry assay was used to analyze DNA double strand breaks, cell cycle alterations, and apoptosis.
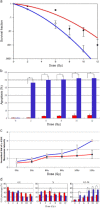
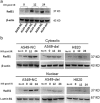
Results: A549 had a higher survival factor (SF)2 (0.66 vs. 0.44) and lower α/β value (4.07 vs. 9.01). Compared with the A549 cell, the H820 cell exhibited defective arrest in the S-phase, a higher rate of G2/M accumulation, early apoptosis, and residual γ-H2AX. Downregulated Rad51 expression decreased SF2 (0.42 vs. 0.31) and increased the α/β ratio (7.51 vs. 10.5), G2/M accumulation, early apoptosis, and γ-H2AX in two cell lines. H820 had a low IR-induced Rad51 expression and nuclear translocation. Exogenous expression of the ΔE746-E750 deletion mutant EGFR caused the A549 cell to become more radiosensitive.
Conclusions: An EGFR mutated NSCLC cell line is sensitive to IR , which is correlated with reduced IR-induced Rad51 expression and nuclear translocation. The signaling pathway of EGFR maintaining Rad51 protein levels maybe a novel lung cancer therapeutic target to overcome radioresistance.
Keywords: Epidermal growth factor receptor; Rad51; mutation; non‐small cell lung cancer; radiosensitivity.
Figures
 ) A549, (
) A549, ( )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
) 
 )
)  )
) 
 )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
) 
 )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
) 
Similar articles
-
Somatic mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) abrogate EGFR-mediated radioprotection in non-small cell lung carcinoma.Cancer Res. 2007 Jun 1;67(11):5267-74. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0242. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17545606
-
Non-small-cell lung cancers with kinase domain mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor are sensitive to ionizing radiation.Cancer Res. 2006 Oct 1;66(19):9601-8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2627. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 17018617
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer cells are associated with increased radiosensitivity in vitro.Cancer Manag Res. 2018 Sep 13;10:3551-3560. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S165831. eCollection 2018. Cancer Manag Res. 2018. PMID: 30271203 Free PMC article.
-
Nimotuzumab enhances radiation sensitivity of NSCLC H292 cells in vitro by blocking epidermal growth factor receptor nuclear translocation and inhibiting radiation-induced DNA damage repair.Onco Targets Ther. 2015 Apr 13;8:809-18. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S77283. eCollection 2015. Onco Targets Ther. 2015. PMID: 25926742 Free PMC article.
-
Ionizing Radiation Protein Biomarkers in Normal Tissue and Their Correlation to Radiosensitivity: A Systematic Review.J Pers Med. 2021 Feb 19;11(2):140. doi: 10.3390/jpm11020140. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 33669522 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential expression of lung adenocarcinoma transcriptome with signature of tobacco exposure.J Appl Genet. 2020 Sep;61(3):421-437. doi: 10.1007/s13353-020-00569-1. Epub 2020 Jun 20. J Appl Genet. 2020. PMID: 32564237 Free PMC article.
-
Radiosensitivity index emerges as a potential biomarker for combined radiotherapy and immunotherapy.NPJ Genom Med. 2021 Jun 2;6(1):40. doi: 10.1038/s41525-021-00200-0. NPJ Genom Med. 2021. PMID: 34078917 Free PMC article.
-
Y Chromosome LncRNA Are Involved in Radiation Response of Male Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells.Cancer Res. 2020 Oct 1;80(19):4046-4057. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-4032. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32616503 Free PMC article.
-
Unique MicroRNA and mRNA Interactions in EGFR-Mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma.J Clin Med. 2018 Nov 6;7(11):419. doi: 10.3390/jcm7110419. J Clin Med. 2018. PMID: 30404194 Free PMC article.
-
SETD2 regulates gene transcription patterns and is associated with radiosensitivity in lung adenocarcinoma.Front Genet. 2022 Aug 10;13:935601. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.935601. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36035179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 2012; 62: 10–29. - PubMed
-
- Yang P, Allen MS, Aubry MC et al Clinical features of 5,628 primary lung cancer patients: Experience at Mayo Clinnic from 1997 to 2003. Chest 2005; 128: 452–462. - PubMed
-
- Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K et al Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non‐small‐cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med 2010; 362: 2380–2388. - PubMed
-
- Ang KK, Bonner JA, Curran WJ, Harari PM, Langer CJ. The Expanding Role of EGFR‐targeted Therapies in NSCLC and Head and Neck Cancer. American Academy of CME, Houston: 2006.
-
- Raymond E, Faivre S, Armand JP. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase as a target for anticancer therapy. Drugs 2000; 60 (Suppl. 1): 15–23. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

