Rad51 in regulating the radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer with different epidermal growth factor receptor mutation status
- PMID: 26816539
- PMCID: PMC4718133
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.12274
Rad51 in regulating the radiosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer with different epidermal growth factor receptor mutation status
Abstract
Background: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring kinase-domain mutations in epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR) has been observed to be sensitive to ionizing radiation (IR). We explore Rad51-dependent homologous recombination (HR) DNA repair in regulating radiosensitivity in two NSCLC cell lines with different EGFR mutation status.
Methods: NSCLC cell lines, wild-type EGFR A549 and mutant EGFR H820 with an in-frame deletion in exon 19 of EGFR (ΔE746-E750), were cultured. Radiosensitivity was estimated by colony forming assay. Rad51 expression was evaluated by quantitative real time-polymerase chain reaction and Western-blot. Lentiviral small hairpin ribonucleic acid-Rad51 and ΔE746-E750 deletion mutant EGFR were constructed and transfected into cells. Flowcytometry assay was used to analyze DNA double strand breaks, cell cycle alterations, and apoptosis.
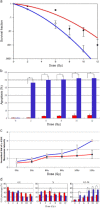
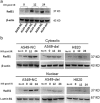
Results: A549 had a higher survival factor (SF)2 (0.66 vs. 0.44) and lower α/β value (4.07 vs. 9.01). Compared with the A549 cell, the H820 cell exhibited defective arrest in the S-phase, a higher rate of G2/M accumulation, early apoptosis, and residual γ-H2AX. Downregulated Rad51 expression decreased SF2 (0.42 vs. 0.31) and increased the α/β ratio (7.51 vs. 10.5), G2/M accumulation, early apoptosis, and γ-H2AX in two cell lines. H820 had a low IR-induced Rad51 expression and nuclear translocation. Exogenous expression of the ΔE746-E750 deletion mutant EGFR caused the A549 cell to become more radiosensitive.
Conclusions: An EGFR mutated NSCLC cell line is sensitive to IR , which is correlated with reduced IR-induced Rad51 expression and nuclear translocation. The signaling pathway of EGFR maintaining Rad51 protein levels maybe a novel lung cancer therapeutic target to overcome radioresistance.
Keywords: Epidermal growth factor receptor; Rad51; mutation; non‐small cell lung cancer; radiosensitivity.
Figures
 ) A549, (
) A549, ( )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
) 
 )
)  )
) 
 )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
) 
 )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
)  )
) 
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 2012; 62: 10–29. - PubMed
-
- Yang P, Allen MS, Aubry MC et al Clinical features of 5,628 primary lung cancer patients: Experience at Mayo Clinnic from 1997 to 2003. Chest 2005; 128: 452–462. - PubMed
-
- Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K et al Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non‐small‐cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med 2010; 362: 2380–2388. - PubMed
-
- Ang KK, Bonner JA, Curran WJ, Harari PM, Langer CJ. The Expanding Role of EGFR‐targeted Therapies in NSCLC and Head and Neck Cancer. American Academy of CME, Houston: 2006.
-
- Raymond E, Faivre S, Armand JP. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase as a target for anticancer therapy. Drugs 2000; 60 (Suppl. 1): 15–23. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

