Bonding values of two contemporary ceramic inlay materials to dentin following simulated aging
- PMID: 26816574
- PMCID: PMC4722148
- DOI: 10.4047/jap.2015.7.6.446
Bonding values of two contemporary ceramic inlay materials to dentin following simulated aging
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the push-out bond strength of feldspar and zirconia-based ceramic inlays bonded to dentin with different resin cements following simulated aging.
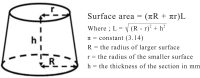
Materials and methods: Occlusal cavities in 80 extracted molars were restored in 2 groups (n=40) with CAD/CAM feldspar (Vitablocs Trilux forte) (FP) and zirconia-based (Ceramill Zi) (ZR) ceramic inlays. The fabricated inlays were luted in 2 subgroups (n=20) with either etch-and-bond (RelyX Ultimate Clicker) (EB) or self-adhesive (RelyX Unicem Aplicap) (SA) resin cement. Ten inlays in each subgroup were subjected to 3,500 thermal cycles and 24,000 loading cycles, while the other 10 served as control. Horizontal 3 mm thick specimens were cut out of the restored teeth for push out bond strength testing. Bond strength data were statistically analyzed using 1-way ANOVA and Tukey's comparisons at α=.05. The mode of ceramic-cement-dentin bond failure for each specimen was also assessed.
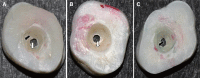
Results: No statistically significant differences were noticed between FP and ZR bond strength to dentin in all subgroups (ANOVA, P=.05113). No differences were noticed between EB and SA (Tukey's, P>.05) bonded to either type of ceramics. Both adhesive and mixed modes of bond failure were dominant for non-aged inlays. Simulated aging had no significant effect on bond strength values (Tukey's, P>.05) of all ceramic-cement combinations although the adhesive mode of bond failure became more common (60-80%) in aged inlays.
Conclusion: The suggested cement-ceramic combinations offer comparable bonding performance to dentin substrate either before or after simulated aging that seems to have no adverse effect on the achieved bond.
Keywords: Bonding; Ceramics; Dentin; Inlays; Resin cement.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bond strength and interfacial micromorphology of etch-and-rinse and self-adhesive resin cements to dentin.J Prosthodont. 2012 Feb;21(2):101-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-849X.2011.00794.x. Epub 2011 Nov 1. J Prosthodont. 2012. PMID: 22044733
-
The marginal quality of luted ceramic inserts in bovine teeth and ceramic inlays in extracted molars after occlusal loading.J Adhes Dent. 2005 Autumn;7(3):213-23. J Adhes Dent. 2005. PMID: 16240962
-
Microleakage of ceramic inlays luted with different resin cements and dentin adhesives.J Prosthet Dent. 2009 Oct;102(4):235-41. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3913(09)60161-X. J Prosthet Dent. 2009. PMID: 19782826
-
Dentin bond strengths of two ceramic inlay systems after cementation with three different techniques and one bonding system.J Prosthet Dent. 2003 Mar;89(3):275-81. doi: 10.1067/mpr.2003.37. J Prosthet Dent. 2003. PMID: 12644803 Clinical Trial.
-
Three-dimensional finite element analysis of strength and adhesion of composite resin versus ceramic inlays in molars.J Prosthet Dent. 2008 Feb;99(2):131-40. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3913(08)60029-3. J Prosthet Dent. 2008. PMID: 18262014
Cited by
-
Novel Cavity Disinfectants Containing Quaternary Ammonium Monomer Dimethylaminododecyl Methacrylate.Materials (Basel). 2016 Aug 9;9(8):674. doi: 10.3390/ma9080674. Materials (Basel). 2016. PMID: 28773797 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of bond strength of self-adhesive and self-etch or total-etch resin cement to zirconia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Conserv Dent Endod. 2024 Feb;27(2):113-125. doi: 10.4103/JCDE.JCDE_225_23. Epub 2024 Feb 8. J Conserv Dent Endod. 2024. PMID: 38463466 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Banks RG. Conservative posterior ceramic restorations: a literature review. J Prosthet Dent. 1990;63:619–626. - PubMed
-
- Kawai K, Hayashi M, Torii M, Tsuchitani Y. Marginal adaptability and fit of ceramic milled inlays. J Am Dent Assoc. 1995;126:1414–1419. - PubMed
-
- Krejci I, Lutz F, Reimer M. Marginal adaptation and fit of adhesive ceramic inlays. J Dent. 1993;21:39–46. - PubMed
-
- Thordrup M, Isidor F, Hörsted-Bindslev P. Comparison of marginal fit and microleakage of ceramic and composite inlays: an in vitro study. J Dent. 1994;22:147–153. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

