Higher intake of fruits, vegetables or their fiber reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 26816602
- PMCID: PMC4718092
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.12376
Higher intake of fruits, vegetables or their fiber reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Aims/introduction: Some previous studies reported no significant association of consuming fruit or vegetables, or fruit and vegetables combined, with type 2 diabetes. Others reported that only a greater intake of green leafy vegetables reduced the risk of type 2 diabetes. To further investigate the relationship between them, we carried out a meta-analysis to estimate the independent effects of the intake of fruit, vegetables and fiber on the risk of type 2 diabetes.
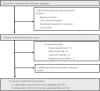
Materials and methods: Searches of MEDLINE and EMBASE for reports of prospective cohort studies published from 1 January 1966 to 21 July 2014 were carried out, checking reference lists, hand-searching journals and contacting experts.
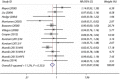
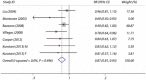
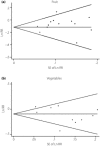
Results: The primary analysis included a total of 23 (11 + 12) articles. The pooled maximum-adjusted relative risk of type 2 diabetes for the highest intake vs the lowest intake were 0.91 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.87-0.96) for total fruits, 0.75 (95% CI 0.66-0.84) for blueberries, 0.87 (95% CI 0.81-0.93) for green leafy vegetables, 0.72 (95% CI 0.57-0.90) for yellow vegetables, 0.82 (95% CI 0.67-0.99) for cruciferous vegetables and 0.93 (95% CI 0.88-0.99) for fruit fiber in these high-quality studies in which scores were seven or greater, and 0.87 (95% CI 0.80-0.94) for vegetable fiber in studies with a follow-up period of 10 years or more.
Conclusions: A higher intake of fruit, especially berries, and green leafy vegetables, yellow vegetables, cruciferous vegetables or their fiber is associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: Meta‐analysis; Nutrition intake; Type 2 diabetes.
Figures


References
-
- Guariguata L, Whiting DR, Hambleton I, et al Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2013 and projections for 2035. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2014; 103: 137–149. - PubMed
-
- Whiting DR, Guariguata L, Weil C, et al IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2011 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2011; 94: 311–321. - PubMed
-
- Shaw JE, Sicree RA, Zimmet PZ. Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2010; 87: 4–14. - PubMed
-
- Steyn NP, Mann J, Bennett PH, et al Diet, nutrition and the prevention of type 2 diabetes. Public Health Nutr 2004; 7: 147–165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

