Selectivity of biopolymer membranes using HepG2 cells
- PMID: 26816630
- PMCID: PMC4669028
- DOI: 10.1093/rb/rbu018
Selectivity of biopolymer membranes using HepG2 cells
Abstract
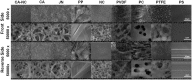
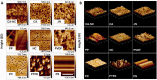
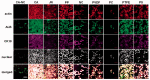
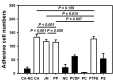
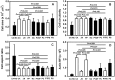
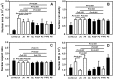
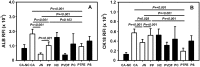
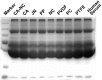
Bioartificial liver (BAL) system has emerged as an alternative treatment to bridge acute liver failure to either liver transplantation or liver regeneration. One of the main reasons that the efficacy of the current BAL systems was not convincing in clinical trials is attributed to the lack of friendly interface between the membrane and the hepatocytes in liver bioreactor, the core unit of BAL system. Here, we systematically compared the biological responses of hepatosarcoma HepG2 cells seeded on eight, commercially available biocompatible membranes made of acetyl cellulose-nitrocellulose mixed cellulose (CA-NC), acetyl cellulose (CA), nylon (JN), polypropylene (PP), nitrocellulose (NC), polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), polycarbonate (PC) and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). Physicochemical analysis and mechanical tests indicated that CA, JN and PP membranes yield high adhesivity and reasonable compressive and/or tensile features with friendly surface topography for cell seeding. Cells prefer to adhere on CA, JN, PP or PTFE membranes with high proliferation rate in spheriod-like shape. Actin, albumin and cytokeratin 18 expressions are favorable for cells on CA or PP membrane, whereas protein filtration is consistent among all the eight membranes. These results further the understandings of cell growth, morphology and spreading, as well as protein filtration on distinct membranes in designing a liver bioreactor.
Keywords: HepG2; bioartificial liver; biocompatible membrane.
Figures
References
-
- Gebhardt R. Metabolic zonation of the liver: regulation and implications for liver function. Pharmacol Ther 1992;53:275–354. - PubMed
-
- Park J, Lee D. Bioartificial liver systems: current status and future perspective. J Biosci Bioeng 2005;99:311–9. - PubMed
-
- Opolon P. High permeability membrane hemodialysis and hemofiltration in acute hepatic coma: experimental and clinical results. Artif Organs 1979;3:354–60. - PubMed
-
- Knell A, Dukes D. Dialysis procedures in acute liver failure. Lancet 1976;2:402–3. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

