The epidemiology of renal trauma
- PMID: 26816762
- PMCID: PMC4708168
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4683.2014.04.11
The epidemiology of renal trauma
Abstract
Introduction: Nonoperative and minimally invasive management techniques for both blunt and penetrating renal trauma have become standard of care over the past decades. We sought to examine the modern epidemiology of renal trauma over the past decade.
Methods: A systematic review of PubMed from the past decade was conducted to examine adult and pediatric renal trauma. A total of 605 articles were identified. Of these, 15 adult and 5 pediatric articles met our a priori search criteria.
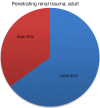
Results: There is a lack of uniform reporting of the renal trauma demographics precluding accurate assessment. Despite this, we were able to elucidate the following details. Renal trauma predominately affects young adult males, and the etiology is predominantly blunt. Among blunt injuries, motor vehicle crashes are most common among adult and pediatric patients. Nonoperative care was utilized in 94.8% of reviewed manuscripts with a 5.4% nephrectomy rate.
Discussion: There do not appear to be any startling changes in the presentation of adult and pediatric renal trauma over the past decade. Nonoperative care continues to be utilized as primary therapy. Increased attention on the reporting of renal trauma demographics is necessary to improve detection of trends.
Conclusions: Increased reporting of the presenting demographics of adult and pediatric renal trauma is encouraged to assist future assessment of epidemiology.
Keywords: Epidemiology; adult; pediatric; renal trauma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evolving Mechanisms of Injury and Management of Pediatric Blunt Renal Trauma--20 Years of Experience.Urology. 2016 Apr;90:159-63. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2016.01.017. Epub 2016 Jan 26. Urology. 2016. PMID: 26825488
-
Contemporary management of high-grade renal trauma: Results from the American Association for the Surgery of Trauma Genitourinary Trauma study.J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2018 Mar;84(3):418-425. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000001796. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2018. PMID: 29298242
-
Pediatric renal injuries: management guidelines from a 25-year experience.J Urol. 2004 Aug;172(2):687-90; discussion 690. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000129316.42953.76. J Urol. 2004. PMID: 15247762
-
Traumatic kidney injuries: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Surg. 2020 Feb;74:13-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2019.12.013. Epub 2019 Dec 21. Int J Surg. 2020. PMID: 31870753
-
Operative and nonoperative management for renal trauma: comparison of outcomes. A systematic review and meta-analysis.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2017 Aug 31;13:1127-1138. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S139194. eCollection 2017. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2017. PMID: 28894376 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Blunt renal trauma in pediatric population.Urol Ann. 2019 Jul-Sep;11(3):241-246. doi: 10.4103/UA.UA_149_18. Urol Ann. 2019. PMID: 31413499 Free PMC article.
-
[Conservative management of grade IV kidney lacerations due to stab wounds].Urologe A. 2022 May;61(5):526-529. doi: 10.1007/s00120-021-01707-1. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Urologe A. 2022. PMID: 34817625 German.
-
Traumatic Blunt Force Renal Injury in a Diseased Horseshoe Kidney with Successful Embolization to Treat Active Bleeding: A Case Report and Literature Review.Case Rep Urol. 2020 Jul 24;2020:8897208. doi: 10.1155/2020/8897208. eCollection 2020. Case Rep Urol. 2020. PMID: 32774982 Free PMC article.
-
Interventional radiology in renal emergencies: a pictorial essay.Emerg Radiol. 2022 Apr;29(2):409-424. doi: 10.1007/s10140-021-02004-2. Epub 2022 Jan 10. Emerg Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35001206
-
Characteristics and outcomes of pediatric blunt renal trauma: a nationwide cohort study in Japan.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2022 Jun;48(3):2047-2057. doi: 10.1007/s00068-021-01795-w. Epub 2021 Sep 25. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2022. PMID: 34562135
References
-
- Shoobridge JJ, Bultitude MF, Koukounaras J, et al. Predicting surgical exploration in renal trauma: assessment and modification of an established nomogram. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 2013;75:819-23. - PubMed
-
- McGuire J, Bultitude MF, Davis P, et al. Predictors of outcome for blunt high grade renal injury treated with conservative intent. J Urol 2011;185:187-91. - PubMed
-
- Figler BD, Malaeb BS, Voelzke B, et al. External validation of a substratification of the American Association for the Surgery of Trauma renal injury scale for grade 4 injuries. J Am Coll Surg 2013;217:924-8. - PubMed
-
- Moolman C, Navsaria PH, Lazarus J, et al. Nonoperative management of penetrating kidney injuries: a prospective audit. J Urol 2012;188:169-73. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous