Intravesical liposome drug delivery and IC/BPS
- PMID: 26816855
- PMCID: PMC4708561
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4683.2015.08.03
Intravesical liposome drug delivery and IC/BPS
Abstract
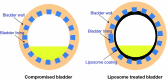
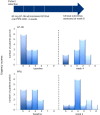
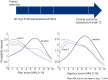
Intravesical therapy has previously shown to be effective in delaying or preventing recurrence of superficial bladder cancer. This local route of drug administration is now demonstrating promise in the treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS) with the benefit of minimal systemic side effects. Liposomes (LPs) are lipid vesicles composed of phospholipid bilayers surrounding an aqueous core. They can incorporate drug molecules, both hydrophobic and hydrophilic, and vastly improve cellular uptake of these drug molecules via endocytosis. Intravesical LPs have therapeutic effects on IC/BPS patients, mainly due to their ability to form a protective lipid film on the urothelial surface and repair the damaged urothelium. This review considers the current status of intravesical LPs and LP mediated drug delivery for the treatment of IC/BPS.
Keywords: Liposome (LP); bladder; interstitial cystitis (IC).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Hsu CC, Chuang YC, Chancellor MB. Intravesical drug delivery for dysfunctional bladder. Int J Urol 2013;20:552-62. - PubMed
-
- Apodaca G. The uroepithelium: not just a passive barrier. Traffic 2004;5:117-28. - PubMed
-
- Cortesi R, Nastruzzi C. Liposomes, micelles and microemulsions as new delivery systems for cytotoxic alkaloids. Pharm Sci Technolo Today 1999;2:288-98. - PubMed
-
- Chuang YC, Lee WC, Lee WC, et al. Intravesical liposome versus oral pentosan polysulfate for interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. J Urol 2009;182:1393-400. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
