Efficacy of Herpes Simplex Virus Vector Encoding the Human Preproenkephalin Gene for Treatment of Facial Pain in Mice
- PMID: 26817032
- PMCID: PMC4874570
- DOI: 10.11607/ofph.1512
Efficacy of Herpes Simplex Virus Vector Encoding the Human Preproenkephalin Gene for Treatment of Facial Pain in Mice
Abstract
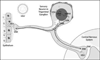
Aims: To determine whether herpes simplex virus-based vectors can efficiently transduce mouse trigeminal ganglion (TG) neurons and attenuate preexisting nerve injury-induced whisker pad mechanical hypersensitivity in a trigeminal inflammatory compression (TIC) neuropathic pain model.
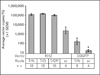
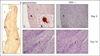
Methods: Tissue transduction efficiencies of replication-conditional and replication-defective vectors to mouse whisker pads after topical administration and subcutaneous injection were assessed using quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR). Tissue tropism and transgene expression were assessed using qPCR and reverse-transcriptase qPCR following topical application of the vectors. Whisker pad mechanical sensitivities of TIC-injured mice were determined using graduated von Frey fibers before and after application of human preproenkephalin expressing replication-conditional vector (KHPE). Data were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and post hoc tests.
Results: Transduction of target TGs was 8- to 50-fold greater after topical application than subcutaneous injection and ≥ 100-fold greater for replication-conditional than replication-defective vectors. Mean KHPE loads remained constant in TGs (4.5-9.8 × 10(4) copies/TG) over 3 weeks but were below quantifiable levels (10 copies/tissue) within 2 weeks of application in other nontarget cephalic tissues examined. Transgene expression in TGs was maximal during 2 weeks after topical application (100-200 cDNA copies/mL) and was below quantifiable levels (1 cDNA copy/mL) in all nontarget tissues. Topical KHPE administration reduced TIC-related mechanical hypersensitivity on whisker pads 4-fold (P < .05) for at least 1 week.
Conclusion: Topically administered KHPE produced a significant antinociceptive effect in the TIC mouse model of chronic facial neuropathic pain. This is the first report in which a gene therapeutic approach reduced trigeminal pain-related behaviors in an established pain state in mice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest related to this study.
Figures


References
-
- Glorioso JC, Mata M, Fink DJ. Therapeutic gene transfer to the nervous system using viral vectors. J Neurovirol. 2003;9:165–172. - PubMed
-
- Kumar S, Ruchi R, James SR, Chidiac EJ. Gene therapy for chronic neuropathic pain: How does it work and where do we stand today? Pain Med. 2011;12:808–822. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

