An Injectable Enzymatically Crosslinked Carboxymethylated Pullulan/Chondroitin Sulfate Hydrogel for Cartilage Tissue Engineering
- PMID: 26817622
- PMCID: PMC4730219
- DOI: 10.1038/srep20014
An Injectable Enzymatically Crosslinked Carboxymethylated Pullulan/Chondroitin Sulfate Hydrogel for Cartilage Tissue Engineering
Abstract
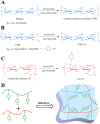
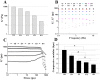
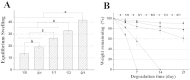
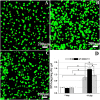
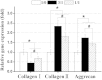
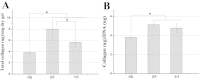
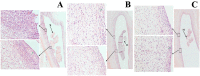
In this study, an enzymatically cross-linked injectable and biodegradable hydrogel system comprising carboxymethyl pullulan-tyramine (CMP-TA) and chondroitin sulfate-tyramine (CS-TA) conjugates was successfully developed under physiological conditions in the presence of both horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) for cartilage tissue engineering (CTTE). The HRP crosslinking method makes this injectable system feasible, minimally invasive and easily translatable for regenerative medicine applications. The physicochemical properties of the mechanically stable hydrogel system can be modulated by varying the weight ratio and concentration of polymer as well as the concentrations of crosslinking reagents. Additionally, the cellular behaviour of porcine auricular chondrocytes encapsulated into CMP-TA/CS-TA hydrogels demonstrates that the hydrogel system has a good cyto-compatibility. Specifically, compared to the CMP-TA hydrogel, these CMP-TA/CS-TA composite hydrogels have enhanced cell proliferation and increased cartilaginous ECM deposition, which significantly facilitate chondrogenesis. Furthermore, histological analysis indicates that the hydrogel system exhibits acceptable tissue compatibility by using a mouse subcutaneous implantation model. Overall, the novel injectable pullulan/chondroitin sulfate composite hydrogels presented here are expected to be useful biomaterial scaffold for regenerating cartilage tissue.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chondrogenesis in injectable enzymatically crosslinked heparin/dextran hydrogels.J Control Release. 2011 May 30;152(1):186-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.01.031. Epub 2011 Feb 1. J Control Release. 2011. PMID: 21291927
-
Development and Evaluation of Gellan Gum/Silk Fibroin/Chondroitin Sulfate Ternary Injectable Hydrogel for Cartilage Tissue Engineering.Biomolecules. 2021 Aug 11;11(8):1184. doi: 10.3390/biom11081184. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34439850 Free PMC article.
-
An injectable platelet lysate-hyaluronic acid hydrogel supports cellular activities and induces chondrogenesis of encapsulated mesenchymal stem cells.Acta Biomater. 2019 Jan 1;83:233-244. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.10.031. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 30366137
-
Horseradish peroxidase-catalysed in situ-forming hydrogels for tissue-engineering applications.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015 Nov;9(11):1225-32. doi: 10.1002/term.1917. Epub 2014 Jun 11. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015. PMID: 24916126 Review.
-
Hydrogel based cartilaginous tissue regeneration: recent insights and technologies.Biomater Sci. 2017 Mar 28;5(4):613-631. doi: 10.1039/c6bm00863a. Biomater Sci. 2017. PMID: 28233881 Review.
Cited by
-
A Bio Polymeric Adhesive Produced by Photo Cross-Linkable Technique.Polymers (Basel). 2016 Aug 10;8(8):292. doi: 10.3390/polym8080292. Polymers (Basel). 2016. Retraction in: Polymers (Basel). 2017 Aug 21;9(8):382. doi: 10.3390/polym9080382. PMID: 30974568 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Current Immunotherapy Strategies for Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Immunoengineering and Delivery Systems.Research (Wash D C). 2023 Oct 17;6:0220. doi: 10.34133/research.0220. eCollection 2023. Research (Wash D C). 2023. PMID: 39902178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combinational regenerative inductive effect of bio-adhesive hybrid hydrogels conjugated with hiPSC-derived myofibers and its derived EVs for volumetric muscle regeneration.Bioact Mater. 2024 Oct 14;43:579-602. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.09.013. eCollection 2025 Jan. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 40115877 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Cellulose-Based Hydrogels: Food Applications.Foods. 2023 Jan 11;12(2):350. doi: 10.3390/foods12020350. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36673441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silk fibroin-based hydrogels for cartilage organoids in osteoarthritis treatment.Theranostics. 2025 Jan 1;15(2):560-584. doi: 10.7150/thno.103491. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 39744693 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jin R. et al.. Enzymatically crosslinked dextran-tyramine hydrogels as injectable scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. Part A. 16, 2429–2440 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Moreira Teixeira L. S. et al.. Self-attaching and cell-attracting in-situ forming dextran-tyramine conjugates hydrogels for arthroscopic cartilage repair. Biomaterials. 33, 3164–3174 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Jin R. et al.. Chondrogenesis in injectable enzymatically crosslinked heparin/dextran hydrogels. J. Controlled Release. 152, 186 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

