Store-operated Ca2+ Entry-associated Regulatory factor (SARAF) Plays an Important Role in the Regulation of Arachidonate-regulated Ca2+ (ARC) Channels
- PMID: 26817842
- PMCID: PMC4807282
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.704940
Store-operated Ca2+ Entry-associated Regulatory factor (SARAF) Plays an Important Role in the Regulation of Arachidonate-regulated Ca2+ (ARC) Channels
Abstract
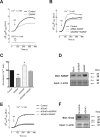
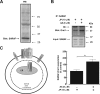
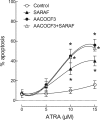
The store-operated Ca(2+)entry-associated regulatory factor (SARAF) has recently been identified as a STIM1 regulatory protein that facilitates slow Ca(2+)-dependent inactivation of store-operated Ca(2+)entry (SOCE). Both the store-operated channels and the store-independent arachidonate-regulated Ca(2+)(ARC) channels are regulated by STIM1. In the present study, we show that, in addition to its location in the endoplasmic reticulum, SARAF is constitutively expressed in the plasma membrane, where it can interact with plasma membrane (PM)-resident ARC forming subunits in the neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y. Using siRNA-based and overexpression approaches we report that SARAF negatively regulates store-independent Ca(2+)entry via the ARC channels. Arachidonic acid (AA) increases the association of PM-resident SARAF with Orai1. Finally, our results indicate that SARAF modulates the ability of AA to promote cell survival in neuroblastoma cells. In addition to revealing new insight into the biology of ARC channels in neuroblastoma cells, these findings provide evidence for an unprecedented location of SARAF in the plasma membrane.
Keywords: ARC channels; SARAF; arachidonic acid (AA) (ARA); calcium channel; calcium release-activated calcium channel protein 1 (ORAI1); protein-protein interaction; stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1).
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Mignen O., and Shuttleworth T. J. (2000) I(ARC), a novel arachidonate-regulated, noncapacitative Ca(2+) entry channel. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 9114–9119 - PubMed
-
- Shuttleworth T. J. (1996) Arachidonic acid activates the noncapacitative entry of Ca2+ during [Ca2+]i oscillations. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 21720–21725 - PubMed
-
- Shuttleworth T. J., Thompson J. L., and Mignen O. (2004) ARC channels: a novel pathway for receptor-activated calcium entry. Physiology 19, 355–361 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

