Recombinant pre-miR-29b for Alzheimer´s disease therapeutics
- PMID: 26818210
- PMCID: PMC4730146
- DOI: 10.1038/srep19946
Recombinant pre-miR-29b for Alzheimer´s disease therapeutics
Abstract
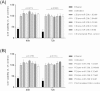
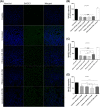
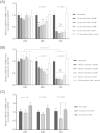
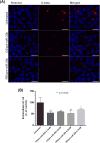
MicroRNAs are arising as the next generation of diagnostic and therapeutic tools for gene silencing. Studies demonstrated that the miR-29 expression is decreased in Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients displaying high levels of human β-secretase (hBACE1). Recent advances toward an effective therapy for AD intend to employ miR-29 to suppress hBACE1 expression and subsequent Amyloid-β (Aβ) peptide. However, delivery of mature miRNA has demonstrated modest efficacy in vitro; therefore, the preparation of highly pure and biologically active pre-miRNA arises as one of the most important challenges in the development of these therapeutic strategies. Recently, we described a new strategy based arginine-affinity chromatography to specifically purify the recombinant pre-miR-29b. Following this strategy, the purified pre-miR-29b was successfully encapsulated into polyplexes that were further delivered in cytoplasm. It was verified that Chitosan/pre-miR-29b and Polyethylenimine/pre-miR-29b systems efficiently delivered pre-miR-29b to N2a695 cells, thus reducing the hBACE1 protein expression (around 78% and 86%, respectively) and Aβ42 levels (approximately 44% and 47%, respectively). Furthermore, pre-miR-29b downregulates the hBACE1 mRNA expression in 80%. Overall, it was demonstrated that the recombinant pre-miR-29b using polyplexes allowed to decrease the hBACE1 and Aβ42 expression levels, improving the currently available methodologies of miRNA-based therapeutics.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-384 regulates both amyloid precursor protein and β-secretase expression and is a potential biomarker for Alzheimer's disease.Int J Mol Med. 2014 Jul;34(1):160-6. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1780. Epub 2014 May 13. Int J Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24827165
-
miR-15b reduces amyloid-β accumulation in SH-SY5Y cell line through targetting NF-κB signaling and BACE1.Biosci Rep. 2018 Nov 13;38(6):BSR20180051. doi: 10.1042/BSR20180051. Print 2018 Dec 21. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29961672 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-29c targets β-site amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme 1 and has a neuroprotective role in vitro and in vivo.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Aug;12(2):3081-8. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3728. Epub 2015 May 5. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25955795
-
The recent updates of therapeutic approaches against aβ for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2011 Aug;294(8):1307-18. doi: 10.1002/ar.21425. Epub 2011 Jun 29. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2011. PMID: 21717585 Review.
-
Alzheimer's disease.Subcell Biochem. 2012;65:329-52. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-5416-4_14. Subcell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 23225010 Review.
Cited by
-
Adulthood blood levels of hsa-miR-29b-3p associate with preterm birth and adult metabolic and cognitive health.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 28;11(1):9203. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88465-4. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33911114 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential Markers of Circulating microRNAs and long non-coding RNAs in Alzheimer's Disease.Aging Dis. 2019 Dec 1;10(6):1293-1301. doi: 10.14336/AD.2018.1105. eCollection 2019 Dec. Aging Dis. 2019. PMID: 31788340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early Life Stress and Epigenetics in Late-onset Alzheimer's Dementia: A Systematic Review.Curr Genomics. 2018 Nov;19(7):522-602. doi: 10.2174/1389202919666171229145156. Curr Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30386171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel approaches for efficient in vivo fermentation production of noncoding RNAs.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Mar;104(5):1927-1937. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-10350-3. Epub 2020 Jan 17. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31953559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of MicroRNAs in Aβ Deposition and Tau Phosphorylation in Alzheimer's Disease.Front Neurol. 2017 Jul 18;8:342. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2017.00342. eCollection 2017. Front Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28769871 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bartels C. L. & Tsongalis G. J. MicroRNAs: novel biomarkers for human cancer. Clin Chem 55, 623–31 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Selbach M. et al.. Widespread changes in protein synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature 455, 58–63 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431, 350–5 (2004). - PubMed
-
- He L. & Hannon G. J. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet 5, 522–31 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

