Comparison of hypoxia-activated prodrug evofosfamide (TH-302) and ifosfamide in preclinical non-small cell lung cancer models
- PMID: 26818215
- PMCID: PMC5036787
- DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2016.1139268
Comparison of hypoxia-activated prodrug evofosfamide (TH-302) and ifosfamide in preclinical non-small cell lung cancer models
Abstract
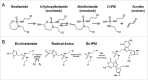
Evofosfamide (TH-302) is a hypoxia-activated prodrug of the cytotoxin bromo-isophosphoramide. In hypoxic conditions Br-IPM is released and alkylates DNA. Ifosfamide is a chloro-isophosphoramide prodrug activated by hepatic Cytochrome P450 enzymes. Both compounds are used for the treatment of cancer. Ifosfamide has been approved by the FDA while evofosfamide is currently in the late stage of clinical development. The purpose of this study is to compare efficacy and safety profile of evofosfamide and ifosfamide in preclinical non-small cell lung cancer H460 xenograft models. Immunocompetent CD-1 mice and H460 tumor-bearing immunocompromised nude mice were used to investigate the safety profile. The efficacy of evofosfamide or ifosfamide, alone, and in combination with docetaxel or sunitinib was compared in ectopic and intrapleural othortopic H460 xenograft models in animals exposed to ambient air or different oxygen concentration breathing conditions. At an equal body weight loss level, evofosfamide showed greater or comparable efficacy in both ectopic and orthotopic H460 xenograft models. Evofosfamide, but not ifosfamide, exhibited controlled oxygen concentration breathing condition-dependent antitumor activity. However, at an equal body weight loss level, ifosfamide yielded severe hematologic toxicity when compared to evofosfamide, both in monotherapy and in combination with docetaxel. At an equal hematoxicity level, evofosfamide showed superior antitumor activity. These results indicate that evofosfamide shows superior or comparable efficacy and a favorable safety profile when compared to ifosfamide in preclinical human lung carcinoma models. This finding is consistent with multiple clinical trials of evofosfamide as a single agent, or in combination therapy, which demonstrated both anti-tumor activity and safety profile without severe myelosuppression.
Keywords: Evofosfamide; hypoxia; hypoxia-activated prodrug; ifosfamide; non-small cell lung cancer; xenograft.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficacy of the hypoxia-activated prodrug evofosfamide (TH-302) in nasopharyngeal carcinoma in vitro and in vivo.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2018 May 3;38(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s40880-018-0285-0. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2018. PMID: 29764490 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer efficacy of the hypoxia-activated prodrug evofosfamide (TH-302) in osteolytic breast cancer murine models.Cancer Med. 2016 Mar;5(3):534-45. doi: 10.1002/cam4.599. Epub 2016 Jan 9. Cancer Med. 2016. PMID: 26749324 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer efficacy of the hypoxia-activated prodrug evofosfamide is enhanced in combination with proapoptotic receptor agonists against osteosarcoma.Cancer Med. 2017 Sep;6(9):2164-2176. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1115. Epub 2017 Aug 10. Cancer Med. 2017. PMID: 28799237 Free PMC article.
-
Evofosfamide, a new horizon in the treatment of pancreatic cancer.Anticancer Drugs. 2016 Sep;27(8):723-5. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000386. Anticancer Drugs. 2016. PMID: 27232101 Review.
-
Overview of ifosfamide in small cell and non-small cell lung cancer.Semin Oncol. 1990 Apr;17(2 Suppl 4):24-30. Semin Oncol. 1990. PMID: 2159187 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of Hypoxia on Tumor Heterogeneity, DNA Repair, and Cancer Therapy: From Molecular Insights to Therapeutic Strategies.Cells. 2025 Jul 10;14(14):1057. doi: 10.3390/cells14141057. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40710312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Hypoxia-Activated Prodrug TH-302: Exploiting Hypoxia in Cancer Therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 19;12:636892. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.636892. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33953675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia-activated prodrug and antiangiogenic therapies cooperatively treat pancreatic cancer but elicit immunosuppressive G-MDSC infiltration.JCI Insight. 2024 Jan 9;9(1):e169150. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.169150. JCI Insight. 2024. PMID: 37988164 Free PMC article.
-
Combining hypoxia-activated prodrugs and radiotherapy in silico: Impact of treatment scheduling and the intra-tumoural oxygen landscape.PLoS Comput Biol. 2020 Aug 3;16(8):e1008041. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008041. eCollection 2020 Aug. PLoS Comput Biol. 2020. PMID: 32745136 Free PMC article.
-
Proteoglycan-targeting applied to hypoxia-activated prodrug therapy in chondrosarcoma: first proof-of-concept.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 27;8(56):95824-95840. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21337. eCollection 2017 Nov 10. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29221170 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith Williams, Introduction to the Principles of Drug Design and Action, 4th Ed, USA: Taylor and Francis Group, 216-30.
-
- Rautio J, Kumpulainen H, Heimbach T, Oliyai R, Oh D, Jaervinen T, Savolainen J. Prodrugs: design and clinical applications. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2008; 7:255-70; PMID:18219308; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrd2468 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Huttunen KM, Raunio H, Rautio J: Prodrugs – from serendipity to rational design. Pharmacol Rev 2011; 63:750-71; PMID:21737530; http://dx.doi.org/10.1124/pr.110.003459 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stella VJ. Prodrugs: Some thoughts and current issues. J Pharm Sci 2010; 99:4755-65; PMID:20821387; http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jps.22205 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brade WP, Herdrich K, Varini M. Ifosfamide- pharmacology, safety and therapeutic potential. Cancer Treat Rev 1985; 12:1-47; PMID:3896483; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0305-7372(85)90011-8 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
