Impact of resistance exercise on ribosome biogenesis is acutely regulated by post-exercise recovery strategies
- PMID: 26818586
- PMCID: PMC4760384
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.12670
Impact of resistance exercise on ribosome biogenesis is acutely regulated by post-exercise recovery strategies
Abstract
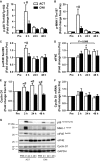
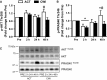
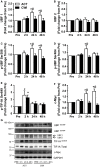
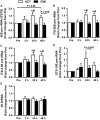
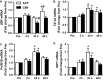
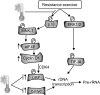
Muscle hypertrophy occurs following increased protein synthesis, which requires activation of the ribosomal complex. Additionally, increased translational capacity via elevated ribosomal RNA (rRNA) synthesis has also been implicated in resistance training-induced skeletal muscle hypertrophy. The time course of ribosome biogenesis following resistance exercise (RE) and the impact exerted by differing recovery strategies remains unknown. In the present study, the activation of transcriptional regulators, the expression levels of pre-rRNA, and mature rRNA components were measured through 48 h after a single-bout RE. In addition, the effects of either low-intensity cycling (active recovery, ACT) or a cold-water immersion (CWI) recovery strategy were compared. Nine male subjects performed two bouts of high-load RE randomized to be followed by 10 min of either ACT or CWI. Muscle biopsies were collected before RE and at 2, 24, and 48 h after RE. RE increased the phosphorylation of the p38-MNK1-eIF4E axis, an effect only evident with ACT recovery. Downstream, cyclin D1 protein, total eIF4E, upstream binding factor 1 (UBF1), and c-Myc proteins were all increased only after RE with ACT. This corresponded with elevated abundance of the pre-rRNAs (45S, ITS-28S, ITS-5.8S, and ETS-18S) from 24 h after RE with ACT. In conclusion, coordinated upstream signaling and activation of transcriptional factors stimulated pre-rRNA expression after RE. CWI, as a recovery strategy, markedly blunted these events, suggesting that suppressed ribosome biogenesis may be one factor contributing to the impaired hypertrophic response observed when CWI is used regularly after exercise.
Keywords: Cyclin D1; hypertrophy; pre‐rRNA; ribosomal RNA; skeletal muscle; upstream binding factor.
© 2016 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American Physiological Society and The Physiological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Consecutive bouts of electrical stimulation-induced contractions alter ribosome biogenesis in rat skeletal muscle.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019 Jun 1;126(6):1673-1680. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00665.2018. Epub 2019 Apr 18. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019. PMID: 30998122
-
Ribosome biogenesis adaptation in resistance training-induced human skeletal muscle hypertrophy.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Jul 1;309(1):E72-83. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00050.2015. Epub 2015 May 12. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 25968575 Clinical Trial.
-
Post-exercise hot-water immersion is not effective for ribosome biogenesis in rat skeletal muscle.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2024 Dec 1;327(6):R601-R615. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00068.2024. Epub 2024 Nov 4. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39495238
-
Revisiting the roles of protein synthesis during skeletal muscle hypertrophy induced by exercise.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2019 Nov 1;317(5):R709-R718. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00162.2019. Epub 2019 Sep 11. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31508978 Review.
-
The Influence of Post-Exercise Cold-Water Immersion on Adaptive Responses to Exercise: A Review of the Literature.Sports Med. 2018 Jun;48(6):1369-1387. doi: 10.1007/s40279-018-0910-8. Sports Med. 2018. PMID: 29627884 Review.
Cited by
-
The cold truth: the role of cryotherapy in the treatment of injury and recovery from exercise.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2021 Aug;121(8):2125-2142. doi: 10.1007/s00421-021-04683-8. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33877402 Review.
-
The Degree of Aminoacidemia after Dairy Protein Ingestion Does Not Modulate the Postexercise Anabolic Response in Young Men: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Nutr. 2019 Sep 1;149(9):1511-1522. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxz099. J Nutr. 2019. PMID: 31152658 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Effects of Cold Water Immersion and Active Recovery on Molecular Factors That Regulate Growth and Remodeling of Skeletal Muscle After Resistance Exercise.Front Physiol. 2020 Jun 30;11:737. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00737. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32695024 Free PMC article.
-
Postexercise cooling impairs muscle protein synthesis rates in recreational athletes.J Physiol. 2020 Feb;598(4):755-772. doi: 10.1113/JP278996. Epub 2019 Dec 29. J Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31788800 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Ribosome Biogenesis in Skeletal Muscle Hypertrophy.Physiology (Bethesda). 2019 Jan 1;34(1):30-42. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00034.2018. Physiology (Bethesda). 2019. PMID: 30540235 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ayrault, O. , Andrique L., Fauvin D., Eymin B., Gazzeri S., and Seite P.. 2006. Human tumor suppressor p14ARF negatively regulates rRNA transcription and inhibits UBF1 transcription factor phosphorylation. Oncogene 25:7577–7586. - PubMed
-
- Chan, J. C. , Hannan K. M., Riddell K., Ng P. Y., Peck A., Lee R. S., et al. 2011. AKT promotes rRNA synthesis and cooperates with c‐MYC to stimulate ribosome biogenesis in cancer. Sci. Signal. 4:ra56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

