Fully integrated wearable sensor arrays for multiplexed in situ perspiration analysis
- PMID: 26819044
- PMCID: PMC4996079
- DOI: 10.1038/nature16521
Fully integrated wearable sensor arrays for multiplexed in situ perspiration analysis
Abstract
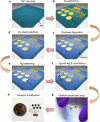
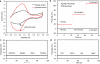
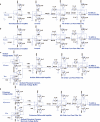
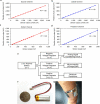
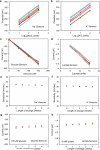
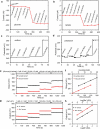
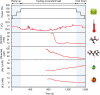
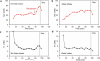
Wearable sensor technologies are essential to the realization of personalized medicine through continuously monitoring an individual's state of health. Sampling human sweat, which is rich in physiological information, could enable non-invasive monitoring. Previously reported sweat-based and other non-invasive biosensors either can only monitor a single analyte at a time or lack on-site signal processing circuitry and sensor calibration mechanisms for accurate analysis of the physiological state. Given the complexity of sweat secretion, simultaneous and multiplexed screening of target biomarkers is critical and requires full system integration to ensure the accuracy of measurements. Here we present a mechanically flexible and fully integrated (that is, no external analysis is needed) sensor array for multiplexed in situ perspiration analysis, which simultaneously and selectively measures sweat metabolites (such as glucose and lactate) and electrolytes (such as sodium and potassium ions), as well as the skin temperature (to calibrate the response of the sensors). Our work bridges the technological gap between signal transduction, conditioning (amplification and filtering), processing and wireless transmission in wearable biosensors by merging plastic-based sensors that interface with the skin with silicon integrated circuits consolidated on a flexible circuit board for complex signal processing. This application could not have been realized using either of these technologies alone owing to their respective inherent limitations. The wearable system is used to measure the detailed sweat profile of human subjects engaged in prolonged indoor and outdoor physical activities, and to make a real-time assessment of the physiological state of the subjects. This platform enables a wide range of personalized diagnostic and physiological monitoring applications.
Figures


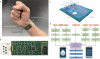

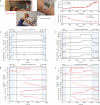

Comment in
-
Bioanalytical devices: Technological leap for sweat sensing.Nature. 2016 Jan 28;529(7587):475-6. doi: 10.1038/529475a. Nature. 2016. PMID: 26819041 No abstract available.
-
Editors' Digest - Basic Science A Wearable Sweat Analyzer for Continuous Electrolyte Monitoring.Perit Dial Int. 2016 Sep 10;36(5):470-1. doi: 10.3747/pdi.2016.00098. Perit Dial Int. 2016. PMID: 27659925 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kim DH, et al. Epidermal electronics. Science. 2011;333:838–843. - PubMed
-
- Lipomi DJ, et al. Skin-like pressure and strain sensors based on transparent elastic films of carbon nanotubes. Nature Nanotechnol. 2011;6:788–792. - PubMed
-
- Takei K, et al. Nanowire active-matrix circuitry for low-voltage macroscale artificial skin. Nature Mater. 2010;9:821–826. - PubMed
-
- Wu W, et al. Piezoelectricity of single-atomic-layer MoS2 for energy conversion and piezotronics. Nature. 2014;514:470–474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

