Mapping the genomic architecture of adaptive traits with interspecific introgressive origin: a coalescent-based approach
- PMID: 26819241
- PMCID: PMC4895787
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-015-2298-2
Mapping the genomic architecture of adaptive traits with interspecific introgressive origin: a coalescent-based approach
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: 'Mapping the genomic architecture of adaptive traits with interspecific introgressive origin: a coalescent-based approach'.BMC Genomics. 2016 Apr 18;17:292. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2497-5. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27090376 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
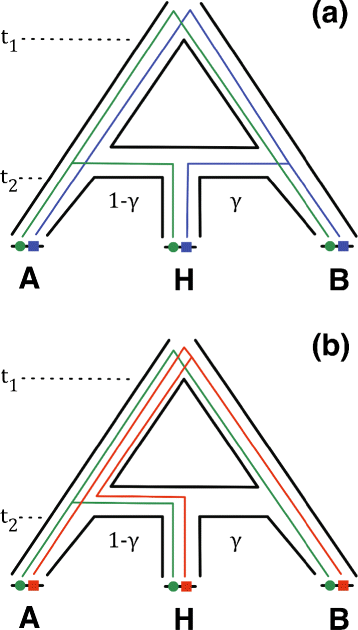
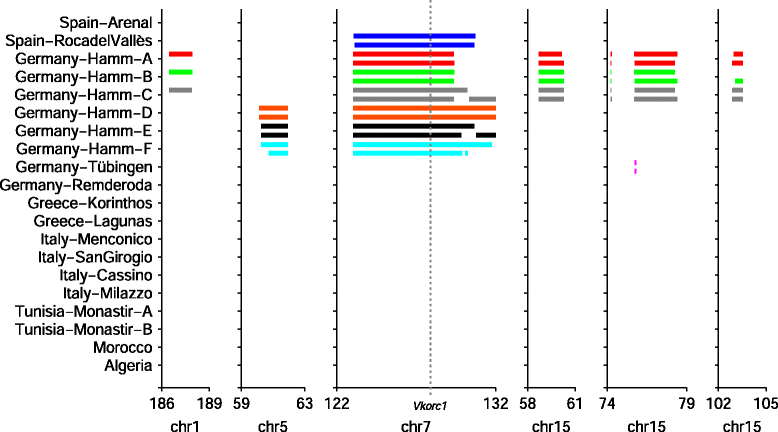
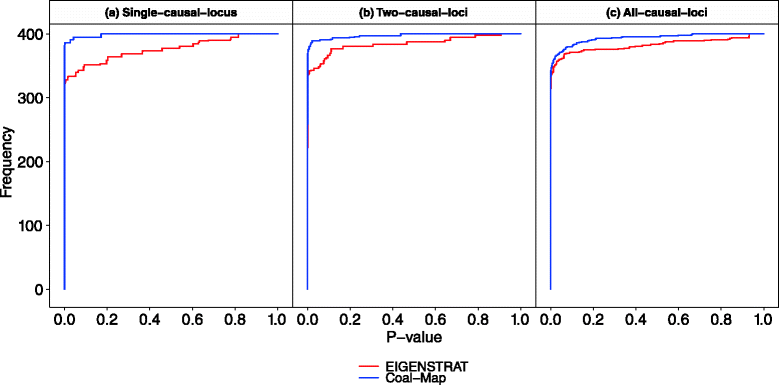
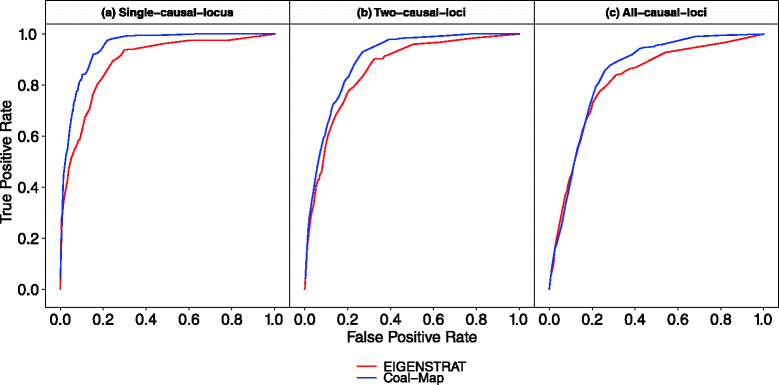
Recent studies of eukaryotes including human and Neandertal, mice, and butterflies have highlighted the major role that interspecific introgression has played in adaptive trait evolution. A common question arises in each case: what is the genomic architecture of the introgressed traits? One common approach that can be used to address this question is association mapping, which looks for genotypic markers that have significant statistical association with a trait. It is well understood that sample relatedness can be a confounding factor in association mapping studies if not properly accounted for. Introgression and other evolutionary processes (e.g., incomplete lineage sorting) typically introduce variation among local genealogies, which can also differ from global sample structure measured across all genomic loci. In contrast, state-of-the-art association mapping methods assume fixed sample relatedness across the genome, which can lead to spurious inference. We therefore propose a new association mapping method called Coal-Map, which uses coalescent-based models to capture local genealogical variation alongside global sample structure. Using simulated and empirical data reflecting a range of evolutionary scenarios, we compare the performance of Coal-Map against EIGENSTRAT, a leading association mapping method in terms of its popularity, power, and type I error control. Our empirical data makes use of hundreds of mouse genomes for which adaptive interspecific introgression has recently been described. We found that Coal-Map's performance is comparable or better than EIGENSTRAT in terms of statistical power and false positive rate. Coal-Map's performance advantage was greatest on model conditions that most closely resembled empirically observed scenarios of adaptive introgression. These conditions had: (1) causal SNPs contained in one or a few introgressed genomic loci and (2) varying rates of gene flow - from high rates to very low rates where incomplete lineage sorting dominated as a primary cause of local genealogical variation.
Figures






Similar articles
-
An HMM-based comparative genomic framework for detecting introgression in eukaryotes.PLoS Comput Biol. 2014 Jun 12;10(6):e1003649. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003649. eCollection 2014 Jun. PLoS Comput Biol. 2014. PMID: 24922281 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of gene-based rare variant association mapping methods for quantitative traits in a bovine population with complex familial relationships.Genet Sel Evol. 2016 Aug 17;48(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s12711-016-0238-5. Genet Sel Evol. 2016. PMID: 27534618 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Power To Dissect Adaptive Traits in Global Sorghum Diversity Using a Nested Association Mapping Population.Genetics. 2017 Jun;206(2):573-585. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.198499. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28592497 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive introgression in animals: examples and comparison to new mutation and standing variation as sources of adaptive variation.Mol Ecol. 2013 Sep;22(18):4606-18. doi: 10.1111/mec.12415. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Mol Ecol. 2013. PMID: 23906376 Review.
-
Association Mapping and Disease: Evolutionary Perspectives.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1910:533-553. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9074-0_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31278676 Review.
Cited by
-
Erratum to: 'Mapping the genomic architecture of adaptive traits with interspecific introgressive origin: a coalescent-based approach'.BMC Genomics. 2016 Apr 18;17:292. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2497-5. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27090376 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

