Microfluidic assay for precise measurements of mouse, rat, and human neutrophil chemotaxis in whole-blood droplets
- PMID: 26819316
- PMCID: PMC6608085
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.5TA0715-310RR
Microfluidic assay for precise measurements of mouse, rat, and human neutrophil chemotaxis in whole-blood droplets
Abstract
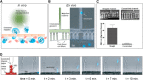
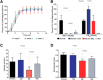
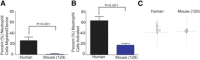
Animal models of human disease differ in innate immune responses to stress, pathogens, or injury. Precise neutrophil phenotype measurements could facilitate interspecies comparisons. However, such phenotype comparisons could not be performed accurately with the use of current assays, as they require the separation of neutrophils from blood using species-specific protocols, and they introduce distinct artifacts. Here, we report a microfluidic technology that enables robust characterization of neutrophil migratory phenotypes in a manner independent of the donor species and performed directly in a droplet of whole blood. The assay relies on the particular ability of neutrophils to deform actively during chemotaxis through microscale channels that block the advance of other blood cells. Neutrophil migration is measured directly in blood, in the presence of other blood cells and serum factors. Our measurements reveal important differences among migration counts, velocity, and directionality among neutrophils from 2 common mouse strains, rats, and humans.
Keywords: inbred lines; migration; neutrophil.
© Society for Leukocyte Biology.
Figures

References
-
- Wipke, B. T. , Allen, P. M. (2001) Essential role of neutrophils in the initiation and progression of a murine model of rheumatoid arthritis. J. Immunol. 167, 1601–1608. - PubMed
-
- Zhao, J. , Li, K. , Wohlford‐Lenane, C. , Agnihothram, S. S. , Fett, C. , Zhao, J. , Gale, M. J. , Jr, Baric, R. S. , Enjuanes, L. , Gallagher, T. , McCray, P. B. , Jr, Perlman, S. (2014) Rapid generation of a mouse model for Middle East respiratory syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111, 4970–4975. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Woodcock, J. , Woosley, R. (2008) The FDA critical path initiative and its influence on new drug development. Annu. Rev. Med. 59, 1–12. - PubMed
-
- Haley, P. J. (2003) Species differences in the structure and function of the immune system. Toxicology 188, 49–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

