4-Isopropyl-2,6-bis(1-phenylethyl)aniline 1, an Analogue of KTH-13 Isolated from Cordyceps bassiana, Inhibits the NF-κB-Mediated Inflammatory Response
- PMID: 26819495
- PMCID: PMC4706927
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/143025
4-Isopropyl-2,6-bis(1-phenylethyl)aniline 1, an Analogue of KTH-13 Isolated from Cordyceps bassiana, Inhibits the NF-κB-Mediated Inflammatory Response
Abstract
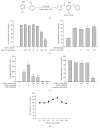
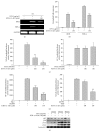
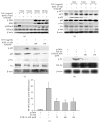
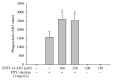
The Cordyceps species has been a good source of compounds with anticancer and anti-inflammatory activities. Recently, we reported a novel compound (4-isopropyl-2,6-bis(1-phenylethyl)phenol, KTH-13) with anticancer activity isolated from Cordyceps bassiana and created several derivatives to increase its pharmacological activity. In this study, we tested one of the KTH-013 derivatives, 4-isopropyl-2,6-bis(1-phenylethyl)aniline 1 (KTH-13-AD1), with regard to anti-inflammatory activity under macrophage-mediated inflammatory conditions. KTH-13-AD1 clearly suppressed the production of nitric oxide (NO) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and sodium nitroprusside- (SNP-) treated macrophage-like cells (RAW264.7 cells). Similarly, this compound also reduced mRNA expression of inducible NO synthase (iNOS) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), as analyzed by RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Interestingly, KTH-13-AD1 strongly diminished NF-κB-mediated luciferase activities and nuclear translocation of NF-κB family proteins. In accordance, KTH-13-AD1 suppressed the upstream signaling pathway of NF-κB activation, including IκBα, IKKα/β, AKT, p85/PI3K, and Src in a time- and dose-dependent manner. The autophosphorylation of Src and NF-κB observed during the overexpression of Src was also suppressed by KTH-13-AD1. These results strongly suggest that KTH-13-AD1 has strong anti-inflammatory features mediated by suppression of the Src/NF-κB regulatory loop.
Figures
Similar articles
-
(5-Hydroxy-4-oxo-4H-pyran-2-yl)methyl 6-hydroxynaphthalene-2-carboxylate, a kojic acid derivative, inhibits inflammatory mediator production via the suppression of Syk/Src and NF-κB activation.Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 May;20(1):37-45. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2014.02.019. Epub 2014 Feb 26. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24583147
-
Quercetin disrupts tyrosine-phosphorylated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and myeloid differentiation factor-88 association, and inhibits MAPK/AP-1 and IKK/NF-κB-induced inflammatory mediators production in RAW 264.7 cells.Immunobiology. 2013 Dec;218(12):1452-67. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2013.04.019. Epub 2013 May 9. Immunobiology. 2013. PMID: 23735482
-
Cordycepin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation by the suppression of NF-kappaB through Akt and p38 inhibition in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells.Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Sep 18;545(2-3):192-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.06.047. Epub 2006 Jun 28. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16899239
-
Syk-Mediated Suppression of Inflammatory Responses by Cordyceps bassiana.Am J Chin Med. 2017;45(6):1217-1232. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X17500677. Epub 2017 Aug 22. Am J Chin Med. 2017. PMID: 28830213
-
Pro-Apoptotic Activity of 4-Isopropyl-2-(1-Phenylethyl) Aniline Isolated from Cordyceps bassiana.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2015 Jul;23(4):367-73. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2015.021. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2015. PMID: 26157554 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Antioxidant and Cytoprotective Effects of (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-(3″-O-methyl) Gallate.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 16;20(16):3993. doi: 10.3390/ijms20163993. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31426336 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory activities of Korean Red Ginseng-derived components.J Ginseng Res. 2016 Oct;40(4):437-444. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2016.08.003. Epub 2016 Aug 24. J Ginseng Res. 2016. PMID: 27746698 Free PMC article.
-
Cordyceps spp.: A Review on Its Immune-Stimulatory and Other Biological Potentials.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Feb 8;11:602364. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.602364. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33628175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Semisynthesis of Derivatives of Oleanolic Acid from Syzygium aromaticum and Their Antinociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Properties.Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:8401843. doi: 10.1155/2016/8401843. Epub 2016 Jun 13. Mediators Inflamm. 2016. PMID: 27382191 Free PMC article.
-
Beauvericin, a cyclic peptide, inhibits inflammatory responses in macrophages by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2017 Jul;21(4):449-456. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2017.21.4.449. Epub 2017 Jun 26. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28706459 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

