CB2 Cannabinoid Receptor Knockout in Mice Impairs Contextual Long-Term Memory and Enhances Spatial Working Memory
- PMID: 26819779
- PMCID: PMC4706977
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/9817089
CB2 Cannabinoid Receptor Knockout in Mice Impairs Contextual Long-Term Memory and Enhances Spatial Working Memory
Abstract
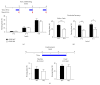
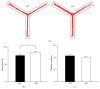
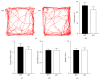
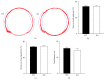
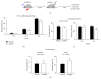
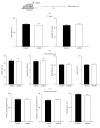
Neurocognitive effects of cannabinoids have been extensively studied with a focus on CB1 cannabinoid receptors because CB1 receptors have been considered the major cannabinoid receptor in the nervous system. However, recent discoveries of CB2 cannabinoid receptors in the brain demand accurate determination of whether and how CB2 receptors are involved in the cognitive effects of cannabinoids. CB2 cannabinoid receptors are primarily involved in immune functions, but also implicated in psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia and depression. Here, we examined the effects of CB2 receptor knockout in mice on memory to determine the roles of CB2 receptors in modulating cognitive function. Behavioral assays revealed that hippocampus-dependent, long-term contextual fear memory was impaired whereas hippocampus-independent, cued fear memory was normal in CB2 receptor knockout mice. These mice also displayed enhanced spatial working memory when tested in a Y-maze. Motor activity and anxiety of CB2 receptor knockout mice were intact when assessed in an open field arena and an elevated zero maze. In contrast to the knockout of CB2 receptors, acute blockade of CB2 receptors by AM603 in C57BL/6J mice had no effect on memory, motor activity, or anxiety. Our results suggest that CB2 cannabinoid receptors play diverse roles in regulating memory depending on memory types and/or brain areas.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chronic activation of CB2 cannabinoid receptors in the hippocampus increases excitatory synaptic transmission.J Physiol. 2015 Feb 15;593(4):871-86. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.286633. Epub 2015 Jan 5. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25504573 Free PMC article.
-
CB1 and CB2 receptors differentially modulate the cognitive impact of maternal immune activation and perinatal cannabinoid exposure.Behav Brain Res. 2025 May 8;485:115543. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2025.115543. Epub 2025 Mar 18. Behav Brain Res. 2025. PMID: 40113177
-
Deletion of CB2 cannabinoid receptors reduces synaptic transmission and long-term potentiation in the mouse hippocampus.Hippocampus. 2016 Mar;26(3):275-81. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22558. Epub 2016 Jan 11. Hippocampus. 2016. PMID: 26663094
-
Discovery of the presence and functional expression of cannabinoid CB2 receptors in brain.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006 Aug;1074:514-36. doi: 10.1196/annals.1369.052. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006. PMID: 17105950 Review.
-
CNS effects of CB2 cannabinoid receptors: beyond neuro-immuno-cannabinoid activity.J Psychopharmacol. 2012 Jan;26(1):92-103. doi: 10.1177/0269881111400652. Epub 2011 Mar 29. J Psychopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21447538 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Review on the Bioactivity of Cannabinoids on Zebrafish Models: Emphasis on Neurodevelopment.Biomedicines. 2022 Jul 28;10(8):1820. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10081820. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36009367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oleoylethanolamide Modulates BDNF-ERK Signaling and Neurogenesis in the Hippocampi of Rats Exposed to Δ9-THC and Ethanol Binge Drinking During Adolescence.Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 Apr 24;12:96. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00096. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31068789 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuation of fear-conditioned analgesia in rats by monoacylglycerol lipase inhibition in the anterior cingulate cortex: Potential role for CB2 receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2020 May;177(10):2240-2255. doi: 10.1111/bph.14976. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Br J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31967664 Free PMC article.
-
TRP Channels as Novel Targets for Endogenous Ligands: Focus on Endocannabinoids and Nociceptive Signalling.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018 Jan 30;16(2):137-150. doi: 10.2174/1570159X15666170424120802. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28440188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CB1 Receptor Signaling in the Brain: Extracting Specificity from Ubiquity.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018 Jan;43(1):4-20. doi: 10.1038/npp.2017.206. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 28862250 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Devane W. A., Dysarz F. A., III, Johnson M. R., Melvin L. S., Howlett A. C. Determination and characterization of a cannabinoid receptor in rat brain. Molecular Pharmacology. 1988;34(5):605–613. - PubMed
-
- Skaper S. D., Buriani A., Dal Toso R., et al. The ALIAmide palmitoylethanolamide and cannabinoids, but not anandamide, are protective in a delayed postglutamate paradigm of excitotoxic death in cerebellar granule neurons. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1996;93(9):3984–3989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.9.3984. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

