Effect of Associative Learning on Memory Spine Formation in Mouse Barrel Cortex
- PMID: 26819780
- PMCID: PMC4706958
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/9828517
Effect of Associative Learning on Memory Spine Formation in Mouse Barrel Cortex
Abstract
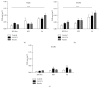
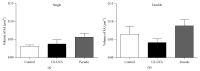
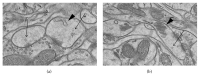
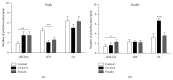
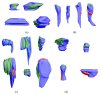
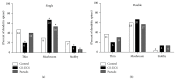
Associative fear learning, in which stimulation of whiskers is paired with mild electric shock to the tail, modifies the barrel cortex, the functional representation of sensory receptors involved in the conditioning, by inducing formation of new inhibitory synapses on single-synapse spines of the cognate barrel hollows and thus producing double-synapse spines. In the barrel cortex of conditioned, pseudoconditioned, and untreated mice, we analyzed the number and morphological features of dendritic spines at various maturation and stability levels: sER-free spines, spines containing smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER), and spines containing spine apparatus. Using stereological analysis of serial sections examined by transmission electron microscopy, we found that the density of double-synapse spines containing spine apparatus was significantly increased in the conditioned mice. Learning also induced enhancement of the postsynaptic density area of inhibitory synapses as well as increase in the number of polyribosomes in such spines. In single-synapse spines, the effects of conditioning were less pronounced and included increase in the number of polyribosomes in sER-free spines. The results suggest that fear learning differentially affects single- and double-synapse spines in the barrel cortex: it promotes maturation and stabilization of double-synapse spines, which might possibly contribute to permanent memory formation, and upregulates protein synthesis in single-synapse spines.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Circadian clock regulates the shape and content of dendritic spines in mouse barrel cortex.PLoS One. 2019 Nov 15;14(11):e0225394. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225394. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31730670 Free PMC article.
-
Fear learning increases the number of polyribosomes associated with excitatory and inhibitory synapses in the barrel cortex.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e54301. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054301. Epub 2013 Feb 14. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23457448 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and plasticity of the double synapse spines in the barrel cortex of the mouse.Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2006;66(2):99-104. doi: 10.55782/ane-2006-1595. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2006. PMID: 16886719
-
Spine dynamics and synapse remodeling during LTP and memory processes.Prog Brain Res. 2008;169:199-207. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(07)00011-8. Prog Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18394475 Review.
-
Dendritic spine dynamics.Annu Rev Physiol. 2009;71:261-82. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.010908.163140. Annu Rev Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19575680 Review.
Cited by
-
Using the Metabolome to Understand the Mechanisms Linking Chronic Arsenic Exposure to Microglia Activation, and Learning and Memory Impairment.Neurotox Res. 2021 Jun;39(3):720-739. doi: 10.1007/s12640-020-00286-x. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Neurotox Res. 2021. PMID: 32955723
-
Circadian Changes of Dendritic Spine Geometry in Mouse Barrel Cortex.Front Neurosci. 2020 Sep 29;14:578881. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.578881. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33117123 Free PMC article.
-
Reward-Related Expectations Trigger Dendritic Spine Plasticity in the Mouse Ventrolateral Orbitofrontal Cortex.J Neurosci. 2019 Jun 5;39(23):4595-4605. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2031-18.2019. Epub 2019 Apr 2. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30940719 Free PMC article.
-
Total Number Is Important: Using the Disector Method in Design-Based Stereology to Understand the Structure of the Rodent Brain.Front Neuroanat. 2018 Mar 5;12:16. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2018.00016. eCollection 2018. Front Neuroanat. 2018. PMID: 29556178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circadian clock regulates the shape and content of dendritic spines in mouse barrel cortex.PLoS One. 2019 Nov 15;14(11):e0225394. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225394. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31730670 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ostroff L. E., Cain C. K., Bedont J., Monfils M. H., LeDoux J. E. Fear and safety learning differentially affect synapse size and dendritic translation in the lateral amygdala. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2010;107(20):9418–9423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0913384107. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

