Efficacy of Retigabine on Acute Limbic Seizures in Adult Rats
- PMID: 26819936
- PMCID: PMC4724852
- DOI: 10.14581/jer.15010
Efficacy of Retigabine on Acute Limbic Seizures in Adult Rats
Abstract
Background and purpose: The efficacy of retigabine (RGB), a positive allosteric modulator of K+ channels indicated for adjunct treatment of partial seizures, was studied in two adult models of kainic acid (KA)-induced status epilepticus to determine it's toleratbility.
Methods: Retigabine was administered systemiclly at high (5 mg/kg) and low (1-2 mg/kg) doses either 30 min prior to or 2 hr after KA-induced status epilepticus. High (1 µg/µL) and low (0.25 µg/µL) concentrations of RGB were also delivered by intrahippocampal microinjection in the presence of KA.
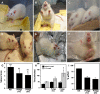
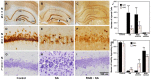
Results: Dose-dependent effects of RGB were observed with both models. Lower doses increased seizure behavior latency and reduced the number of single spikes and synchronized burst events in the electroencephalogram (EEG). Higher doses worsened seizure behavior, produced severe ataxia, and increased spiking activity. Animals treated with RGB that were resistant to seizures did not exhibit significant injury or loss in GluR1 expression; however if stage 5-6 seizures were reached, typical hippocampal injury and depletion of GluR1 subunit protein in vulernable pyramidal fields occurred.
Conclusions: RGB was neuroprotective only if seizures were significantly attenuated. GluR1 was simultaneously suppressed in the resistant granule cell layer in presence of RGB which may weaken excitatory transmission. Biphasic effects observed herein suggest that the human dosage must be carefully scrutinized to produce the optimal clinical response.
Keywords: AMPA receptor; Anticonvulsant; Epilepsy; Hippocampus; Neurodegeneration; Retigabine.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Retigabine calms seizure-induced behavior following status epilepticus.Epilepsy Behav. 2014 Aug;37:123-32. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2014.06.010. Epub 2014 Jul 10. Epilepsy Behav. 2014. PMID: 25016241
-
Phenytoin- and carbamazepine-resistant spontaneous bursting in rat entorhinal cortex is blocked by retigabine in vitro.Epilepsy Res. 2007 May;74(2-3):97-106. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2007.02.001. Epub 2007 Mar 28. Epilepsy Res. 2007. PMID: 17395429
-
Resistance of immature hippocampus to morphologic and physiologic alterations following status epilepticus or kindling.Hippocampus. 2001;11(6):615-25. doi: 10.1002/hipo.1076. Hippocampus. 2001. PMID: 11811655
-
Delayed sclerosis, neuroprotection, and limbic epileptogenesis after status epilepticus in the rat.Epilepsia. 2002;43 Suppl 5:86-95. doi: 10.1046/j.1528-1157.43.s.5.39.x. Epilepsia. 2002. PMID: 12121301
-
Cav3.1 T-type calcium channel modulates the epileptogenicity of hippocampal seizures in the kainic acid-induced temporal lobe epilepsy model.Brain Res. 2015 Oct 5;1622:204-16. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.06.015. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 26111648
Cited by
-
Modulating Behavior in C. elegans Using Electroshock and Antiepileptic Drugs.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 26;11(9):e0163786. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163786. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27668426 Free PMC article.
-
Removal of KCNQ2 from parvalbumin-expressing interneurons improves anti-seizure efficacy of retigabine.Exp Neurol. 2022 Sep;355:114141. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2022.114141. Epub 2022 Jun 9. Exp Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35691372 Free PMC article.
-
egl-4 modulates electroconvulsive seizure duration in C. elegans.Invert Neurosci. 2018 May 30;18(2):8. doi: 10.1007/s10158-018-0211-9. Invert Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29845318 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of brain damage after traumatic brain injury by pharmacological enhancement of KCNQ (Kv7, "M-type") K+ currents in neurons.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2020 Jun;40(6):1256-1273. doi: 10.1177/0271678X19857818. Epub 2019 Jul 4. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2020. PMID: 31272312 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bourgeois BF. Antiepileptic drugs, learning, and behavior in childhood epilepsy. Epilepsia. 1998;39:913–21. - PubMed
-
- Gaitatzis A, Sander JW. The long-term safety of antiepileptic drugs. CNS Drugs. 2013;27:435–55. - PubMed
-
- Halonen T, Nissinen J, Pitkanen A. Effect of lamotrigine treatment on status epilepticus-induced neuronal damage and memory impairment in rat. Epilepsy Res. 2001;46:205–23. - PubMed
-
- Liu Z, Yang Y, Silveira DC, et al. Consequences of recurrent seizures during early brain development. Neuroscience. 1999;92:1443–54. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

