Neutrophils in Cancer: Two Sides of the Same Coin
- PMID: 26819959
- PMCID: PMC4706937
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/983698
Neutrophils in Cancer: Two Sides of the Same Coin
Abstract
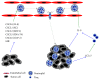
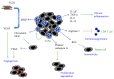
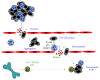
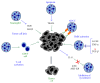
Neutrophils are the most abundant leukocytes in blood and are considered to be the first line of defense during inflammation and infections. In addition, neutrophils are also found infiltrating many types of tumors. Tumor-associated neutrophils (TANs) have relevant roles in malignant disease. Indeed neutrophils may be potent antitumor effector cells. However, increasing clinical evidence shows TANs correlate with poor prognosis. The tumor microenvironment controls neutrophil recruitment and in turn TANs help tumor progression. Hence, TANs can be beneficial or detrimental to the host. It is the purpose of this review to highlight these two sides of the neutrophil coin in cancer and to describe recent studies that provide some light on the mechanisms for neutrophil recruitment to the tumor, for neutrophils supporting tumor progression, and for neutrophil activation to enhance their antitumor functions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neutrophils in the Tumor Microenvironment.Trends Immunol. 2016 Jan;37(1):41-52. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2015.11.008. Epub 2015 Dec 14. Trends Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26700397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer-related circulating and tumor-associated neutrophils - subtypes, sources and function.FEBS J. 2018 Dec;285(23):4316-4342. doi: 10.1111/febs.14524. Epub 2018 Jun 14. FEBS J. 2018. PMID: 29851227 Review.
-
Neutrophils as active regulators of the immune system in the tumor microenvironment.J Leukoc Biol. 2017 Aug;102(2):343-349. doi: 10.1189/jlb.5MR1216-508R. Epub 2017 Mar 6. J Leukoc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28264904 Review.
-
Neutrophils recruit regulatory T-cells into tumors via secretion of CCL17--a new mechanism of impaired antitumor immunity.Int J Cancer. 2014 Sep 1;135(5):1178-86. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28770. Epub 2014 Feb 27. Int J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24501019
-
Tissue-infiltrating neutrophils constitute the major in vivo source of angiogenesis-inducing MMP-9 in the tumor microenvironment.Neoplasia. 2014 Oct 23;16(10):771-88. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2014.08.013. eCollection 2014 Oct. Neoplasia. 2014. PMID: 25379015 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Role of the Tumor Microenvironment in Regulating Pancreatic Cancer Therapy Resistance.Cells. 2022 Sep 21;11(19):2952. doi: 10.3390/cells11192952. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36230914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Mutations Associated with Inflammatory Response Caused by HPV Integration in Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Biomedicines. 2023 Dec 21;12(1):24. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12010024. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38275384 Free PMC article.
-
Drug repurposing of ivermectin abrogates neutrophil extracellular traps and prevents melanoma metastasis.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 5;12:989167. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.989167. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36132145 Free PMC article.
-
Pretreatment Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Lactate Dehydrogenase Predict the Prognosis of Metastatic Cervical Cancer Treated with Combination Immunotherapy.J Oncol. 2022 Oct 18;2022:1828473. doi: 10.1155/2022/1828473. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36304986 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphocyte-mediated Immune Regulation in Health and Disease: The Treg and γδ T Cell Co-conspiracy.Immunol Invest. 2016 Nov;45(8):767-775. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2016.1213278. Epub 2016 Sep 12. Immunol Invest. 2016. PMID: 27617588 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

