miR-655 suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by targeting Prrx1 in triple-negative breast cancer
- PMID: 26820102
- PMCID: PMC4831358
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.12770
miR-655 suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by targeting Prrx1 in triple-negative breast cancer
Retraction in
-
Retraction: miR-655 suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by targeting Prrx1 in triple-negative breast cancer.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Apr;28(8):e18314. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18314. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38655709 Free PMC article.
Abstract
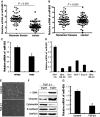
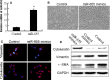
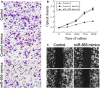
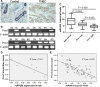
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a highly aggressive breast cancer subtype that lacks effective targeted therapies. The epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a key contributor in the metastatic process. In this study, we found that miR-655 was down-regulated in TNBC, and its expression levels were associated with molecular-based classification and lymph node metastasis in breast cancer. These findings led us to hypothesize that miR-655 overexpression may inhibit EMT and its associated traits of TNBC. Ectopic expression of miR-655 not only induced the up-regulation of cytokeratin and decreased vimentin expression but also suppressed migration and invasion of mesenchymal-like cancer cells accompanied by a morphological shift towards the epithelial phenotype. In addition, we found that miR-655 was negatively correlated with Prrx1 in cell lines and clinical samples. Overexpression of miR-655 significantly suppressed Prrx1, as demonstrated by Prrx1 3'-untranslated region luciferase report assay. Our study demonstrated that miR-655 inhibits the acquisition of the EMT phenotype in TNBC by down-regulating Prrx1, thereby inhibiting cell migration and invasion during cancer progression.
Keywords: Prrx1; epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; miR-655; triple-negative breast cancer.
© 2016 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures



References
-
- Guo W, Wang C, Guo Y, et al RASSF5A, a candidate tumor suppressor, is epigenetically inactivated in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2015; 32: 83–98. - PubMed
-
- Xu XT, Tao ZZ, Song QB, et al SUZ12 RNA interference inhibits the invasion of gastric carcinoma cells. Hepatogastroenterology. 2014; 61: 2416–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

