Incidence of Co-Infections of HIV, Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 and Syphilis in a Large Cohort of Men Who Have Sex with Men in Beijing, China
- PMID: 26820145
- PMCID: PMC4731205
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147422
Incidence of Co-Infections of HIV, Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 and Syphilis in a Large Cohort of Men Who Have Sex with Men in Beijing, China
Abstract
Background: The HIV-epidemic among MSM in China has worsened. In this key population, prevalence of HSV-2 and syphilis infection and co-infection with HIV is high.
Methods: A longitudinal study was conducted (n = 962) in Beijing, China, with three overlapping cohorts (n = 857, 757 and 760) consisting of MSM that were free from pairs of infections of concern (i.e. HIV-HSV-2, HIV-syphilis, HSV-2-syphilis) at baseline to estimate incidence of HIV, HSV-2, syphilis, and those of co-infection.
Results: The incidence of HIV, HSV-2 and syphilis in the overall cohort was 3.90 (95% CI = 2.37, 5.43), 7.87 (95% CI = 5.74, 10.00) and 6.06 (95% CI = 4.18, 7.94) cases per 100 person-years (PYs), respectively. The incidence of HIV-HSV-2, HIV-Syphilis and HSV-2-Syphilis co-infections was 0.30 (95% CI = 0.29, 0.88), 1.02 (95% CI = 0.13, 2.17) and 1.41 (95% CI: 0.04, 2.78) cases per 100 PYs, respectively, in the three sub-cohorts constructed for this study.
Conclusions: The incidence of HIV, HSV-2 and syphilis was very high and those of their co-infections were relatively high. Such co-infections have negative impacts on the HIV/STI epidemics. Prevention practices need to take such co-infections into account.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
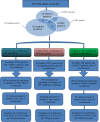
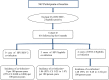
References
-
- Wu ZY. China's assessment and responses to HIV epidemic in MSM. WHO meeting on MSM, Geneva. 08/02/2009.
-
- Jiang J, Cao N, Zhang J, Xia Q, Gong X, Xue H, et al. High prevalence of sexually transmitted diseases among men who have sex with men in Jiangsu Province, China. Sex Transm Dis, 2006,33(2):118–123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

