Identification, expression, and functional analysis of CLE genes in radish (Raphanus sativus L.) storage root
- PMID: 26821718
- PMCID: PMC4895270
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-015-0687-y
Identification, expression, and functional analysis of CLE genes in radish (Raphanus sativus L.) storage root
Abstract
Background: Radish (Raphanus sativus L.) is a widespread agricultural plant forming storage root due to extensive secondary growth which involves cambium proliferation and differentiation of secondary conductive tissues. Closely related to the model object Arabidopsis thaliana, radish is a suitable model for studying processes of secondary growth and storage root development. CLE peptides are a group of peptide phytohormones which play important role in the regulation of primary meristems such as SAM, RAM, and procambium, as well as secondary meristems. However, the role of CLE peptides in lateral growth of root during storage root formation has not been studied to date.
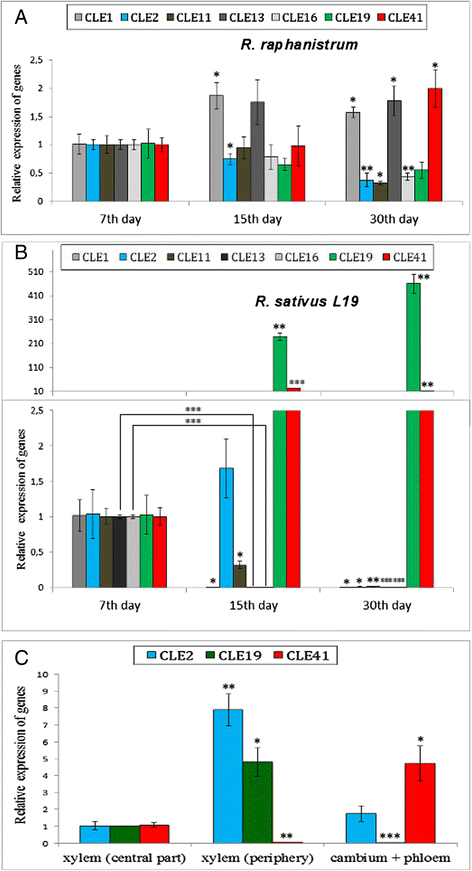
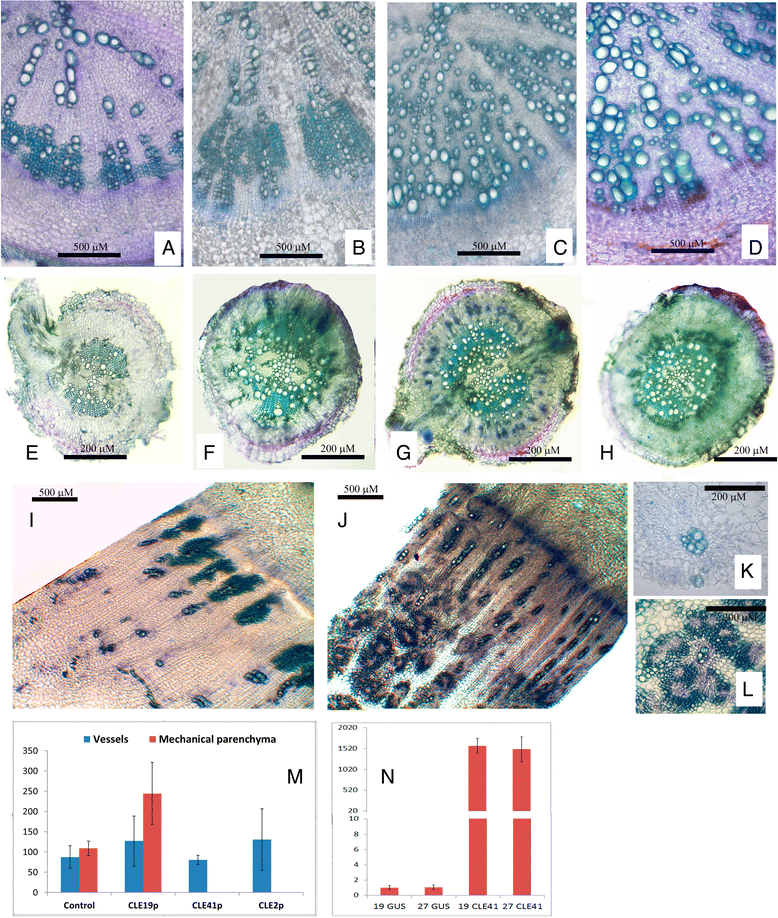
Results: In present work we studied the role of CLE peptides in the development of storage root in radish. We have identified 18 CLE genes of radish (RsCLEs) and measured their expression in various plant organs and also at different stages of root development in R. sativus and Raphanus raphanistrum-its close relative which does not form storage root. We observed significant decline of expression levels for genes RsCLE1, 2, 11, 13, and 16, and also multifold increase of expression levels for genes RsCLE19, and 41 during secondary root growth in R. sativus but not in R. raphanistrum. Expression of RsCLE 2, 19, and 41 in R. sativus root was confined to certain types of tissues while RsCLE1, 11, 13, and 16 expressed throughout the root. Experiments on overexpression of RsCLE2, 19 and 41 or treatment of radish plants with synthetic CLE peptides revealed that CLE19 and CLE2 increase the number of xylem elements, and CLE41 induces the formation of extra cambium foci in secondary xylem. Expression levels of RsCLE2 and 19 strongly decrease in response to exogenous cytokinin, while auxin causes dramatic increase of RsCLE19 expression level and decrease of RsCLE41 expression.
Conclusions: Our data allow us to hypothesize about the role of RsCLE2, 19 and 41 genes in the development of storage root of Raphanus sativus, e.g. RsCLE19 may play a role in auxin-dependent processes of xylem differentiation and RsCLE41 stimulates cambium activity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cytokinin-dependent secondary growth determines root biomass in radish (Raphanus sativus L.).J Exp Bot. 2015 Aug;66(15):4607-19. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv220. Epub 2015 May 15. J Exp Bot. 2015. PMID: 25979997 Free PMC article.
-
Initiation of spontaneous tumors in radish (Raphanus sativus): Cellular, molecular and physiological events.J Plant Physiol. 2015 Jan 15;173:97-104. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2014.07.030. Epub 2014 Sep 18. J Plant Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25462083
-
RsCLE22a regulates taproot growth through an auxin signaling-related pathway in radish (Raphanus sativus L.).J Exp Bot. 2023 Jan 1;74(1):233-250. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erac406. J Exp Bot. 2023. PMID: 36239471
-
CLE peptides in vascular development.J Integr Plant Biol. 2013 Apr;55(4):389-94. doi: 10.1111/jipb.12044. J Integr Plant Biol. 2013. PMID: 23473393 Review.
-
CLE peptides and their signaling pathways in plant development.J Exp Bot. 2016 Aug;67(16):4813-26. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erw208. Epub 2016 May 26. J Exp Bot. 2016. PMID: 27229733 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide identification of CLE gene family and their potential roles in bolting and fruit bearing in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.).BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Mar 19;21(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-02900-2. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 33740893 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide hormones in plants.Mol Hortic. 2025 Jan 23;5(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s43897-024-00134-y. Mol Hortic. 2025. PMID: 39849641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing of RsGL1a and RsGL1b in radish (Raphanus sativus L.).Front Plant Sci. 2022 Oct 13;13:951660. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.951660. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36311091 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Proteomics and Metabolomics Analysis Reveals the Role of Small Signaling Peptide Rapid Alkalinization Factor 34 (RALF34) in Cucumber Roots.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 21;24(8):7654. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087654. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108821 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Functional Analysis of CLAVATA3/EMBRYO SURROUNDING REGION-RELATED (CLE) in Three Populus Species.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 24;26(5):1944. doi: 10.3390/ijms26051944. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076582 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

