The Effect of the Canine ABCB1-1Δ Mutation on Sedation after Intravenous Administration of Acepromazine
- PMID: 26822006
- PMCID: PMC4913601
- DOI: 10.1111/jvim.13827
The Effect of the Canine ABCB1-1Δ Mutation on Sedation after Intravenous Administration of Acepromazine
Abstract
Background: Dog breeds with the ABCB1-1Δ mutation have substantially truncated nonfunctional P-glycoprotein. Dogs homozygous for this mutation (mut/mut) are susceptible to the toxic adverse effects of ivermectin, loperamide, and vincristine. Anecdotal reports suggested ABCB1 mut/mut dogs showed increased depth and duration of acepromazine sedation.
Hypothesis/objectives: That ABCB1 mut/mut dogs have increased depth and duration of sedation after acepromazine IV compared to normal dogs (nor/nor).
Animals: Twenty-nine rough-coated collies were divided into 3 groups of dogs based on their ABCB1 genotype: 10 mut/mut, 10 mut/nor, and 9 nor/nor.
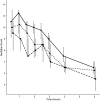
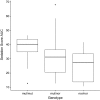
Methods: Dogs were given 0.04 mg/kg of acepromazine IV. Level of sedation, heart rate, respiratory rate, and blood pressure were recorded for 6 hours after acepromazine administration. Area under the curves (AUCs) of the normalized sedation score results were calculated and compared.
Results: The median sedation scores for ABCB1 mut/mut dogs were higher than nor/nor dogs at all time points and were higher in mut/nor dogs for the first 2 hours. These differences were not found to be significant for any individual time point (P > .05). The median sedation score AUC for mut/mut dogs was significantly higher than nor/nor dogs (P = .028), but the AUC for mut/nor dogs was not (P = .45). There were no significant differences between groups for heart rate, respiratory rate, and blood pressure (P > .05).
Conclusions and clinical importance: In ABCB1 mut/mut dogs acepromazine dose rates should be reduced and careful monitoring performed during sedation.
Keywords: Collie; MDR1; P-glycoprotein.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine.
Figures
References
-
- Martinez M, Modric S, Sharkey M, et al. The pharmacogenomics of P‐glycoprotein and its role in veterinary medicine. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 2008;31:285–300. - PubMed
-
- Mealey KL, Bentjen SA, Gay JM, et al. Ivermectin sensitivity in collies is associated with a deletion mutation of the mdr1 gene. Pharmacogenetics 2001;11:727–733. - PubMed
-
- Roulet A, Puel O, Gesta S, et al. MDR1‐deficient genotype in Collie dogs hypersensitive to the P‐glycoprotein substrate ivermectin. Eur J Pharmacol 2003;460:85–91. - PubMed
-
- Nelson OL, Carsten E, Bentjen SA, et al. Ivermectin toxicity in an Australian Shepherd dog with the MDR1 mutation associated with ivermectin sensitivity in Collies. J Vet Intern Med 2003;17:354–356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

