Synergistic growth inhibitory effect of deracoxib with doxorubicin against a canine mammary tumor cell line, CMT-U27
- PMID: 26822118
- PMCID: PMC4873858
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.15-0387
Synergistic growth inhibitory effect of deracoxib with doxorubicin against a canine mammary tumor cell line, CMT-U27
Abstract
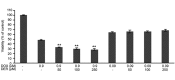
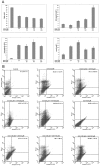
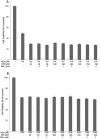
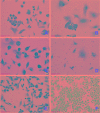
Cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitors have been shown to exert anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor activities on many types of malignant tumors. These anticancer properties make it worthwhile to examine the possible benefit of combining COX inhibitors with other anti-cancer agents. In the present study, we evaluated the potential of deracoxib (DER) in potentiating antitumor activity of doxorubicin (DOX) in canine mammary carcinoma cells (CMT-U27). DER (50-250 µM) enhanced the antiproliferative activity of DOX by reducing the IC50 (approximately 3- to 3.5 fold). Interaction analysis of the data showed that combinations of DOX at 0.9 µM with DER (100-250 µM) produced synergism in the CMT-U27 cell line, with a ratio index ranging from 1.98 to 2.33. In additional studies identifying the mechanism of observed synergistic effect, we found that DER strongly potentiated DOX-caused G0/G1 arrest in cell cycle progression. Also, DER (100-250 µM) augmented apoptosis induction with approximately 1.35- and 1.37- fold increases in apoptotic response caused by DOX in the cells. DER enhanced the antiproliferative effect of DOX in conjunction with induction of apoptosis by modulation of Bcl-2 expression and changes in the cell cycle of the CMT-U27 cell line. Although the exact molecular mechanism of the alterations in the cell cycle and apoptosis observed with DER and DOX combinations require further investigations, the results suggest that the synergistic effect of DOX and DER combinations in CMT therapy may be achieved at relatively lower doses of DOX with lesser side effects. Therefore, combining DER with DOX may prove beneficial in the clinical treatment of canine mammary cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vitro effects of doxorubicin and deracoxib on oxidative-stress-related parameters in canine mammary carcinoma cells.Acta Vet Hung. 2014 Sep;62(3):372-85. doi: 10.1556/AVet.2014.012. Acta Vet Hung. 2014. PMID: 25038953
-
The effects of piroxicam and deracoxib on canine mammary tumour cell line.ScientificWorldJournal. 2012;2012:976740. doi: 10.1100/2012/976740. Epub 2012 Nov 7. ScientificWorldJournal. 2012. PMID: 23251109 Free PMC article.
-
Algerian Propolis Potentiates Doxorubicin Mediated Anticancer Effect Against Human Pancreatic PANC-1 Cancer Cell Line through Cell Cycle Arrest, Apoptosis Induction and P-Glycoprotein Inhibition.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2018;18(3):375-387. doi: 10.2174/1871520618666180110143239. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29318976
-
Anticancer Effects of Mitoquinone via Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Canine Mammary Gland Tumor Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 30;25(9):4923. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094923. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38732133 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulated Signaling Pathways in Canine Mammary Tumor and Human Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Advances and Potential Therapeutic Targets.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 27;26(1):145. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010145. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39796003 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
From Conventional to Precision Therapy in Canine Mammary Cancer: A Comprehensive Review.Front Vet Sci. 2021 Feb 17;8:623800. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.623800. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 33681329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiproliferative Effects of Oxytocin and Desmopressin on Canine Mammary Cancer Cells.Front Vet Sci. 2016 Dec 26;3:119. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2016.00119. eCollection 2016. Front Vet Sci. 2016. PMID: 28083539 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alshafie G. A., Abou-Issa H. M., Seibert K., Harris R. E.2000. Chemotherapeutic evaluation of Celecoxib, a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, in a rat mammary tumor model. Oncol. Rep. 7: 1377–1381. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

