Zebrafish and Medaka: new model organisms for modern biomedical research
- PMID: 26822757
- PMCID: PMC4730764
- DOI: 10.1186/s12929-016-0236-5
Zebrafish and Medaka: new model organisms for modern biomedical research
Abstract
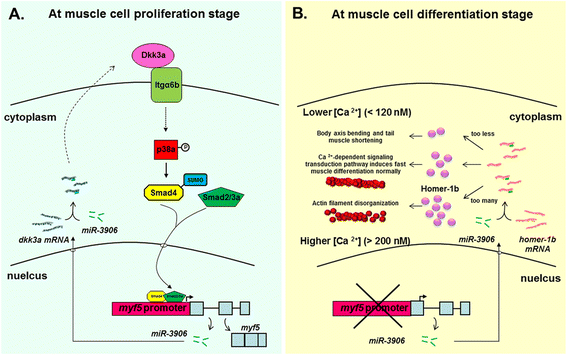
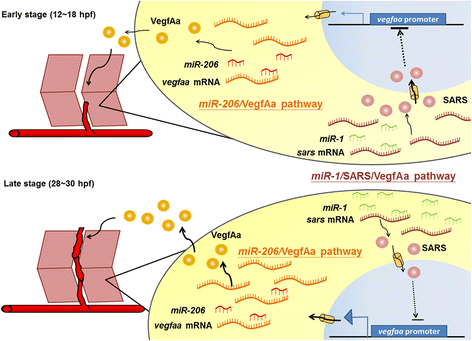
Although they are primitive vertebrates, zebrafish (Danio rerio) and medaka (Oryzias latipes) have surpassed other animals as the most used model organisms based on their many advantages. Studies on gene expression patterns, regulatory cis-elements identification, and gene functions can be facilitated by using zebrafish embryos via a number of techniques, including transgenesis, in vivo transient assay, overexpression by injection of mRNAs, knockdown by injection of morpholino oligonucleotides, knockout and gene editing by CRISPR/Cas9 system and mutagenesis. In addition, transgenic lines of model fish harboring a tissue-specific reporter have become a powerful tool for the study of biological sciences, since it is possible to visualize the dynamic expression of a specific gene in the transparent embryos. In particular, some transgenic fish lines and mutants display defective phenotypes similar to those of human diseases. Therefore, a wide variety of fish model not only sheds light on the molecular mechanisms underlying disease pathogenesis in vivo but also provides a living platform for high-throughput screening of drug candidates. Interestingly, transgenic model fish lines can also be applied as biosensors to detect environmental pollutants, and even as pet fish to display beautiful fluorescent colors. Therefore, transgenic model fish possess a broad spectrum of applications in modern biomedical research, as exampled in the following review.
Figures
References
-
- Hackett PB. The molecular biology of transgenic fish. In: Hochachka PW, Mommsen TP, editors. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Fishes. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science; 1993. pp. 207–240.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

