Potential biological efficacy of Pinus plant species against oxidative, inflammatory and microbial disorders
- PMID: 26822870
- PMCID: PMC4730770
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-016-1011-6
Potential biological efficacy of Pinus plant species against oxidative, inflammatory and microbial disorders
Abstract
Background: Traditionally, Pine has been used to treat oxidative and inflammatory disorders. The study was aimed to investigate biological potential of phytoconstituents of Pinus plant species: Pinus roxburghii, Pinus wallichiana and Pinus gerardiana using in-vitro antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial methods.
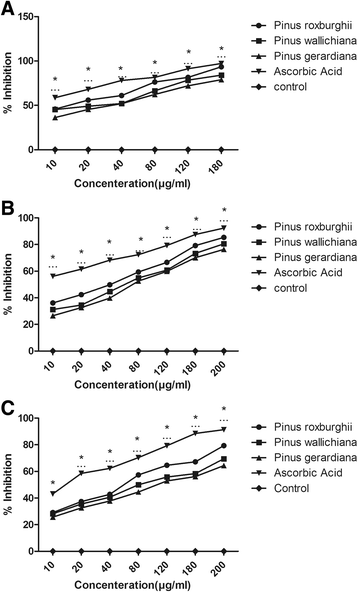
Method: The hydro-alcoholic extraction of dried plant: stem bark was done and the antioxidant activity was evaluated using free radical scavenging methods for 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl, (DPPH), nitric oxide and hydrogen peroxide radicals, reducing power assays, and total antioxidant capacity. Anti-inflammatory activity was carried out using albumin denaturation and HRBC membrane stabilization assays. Antimicrobial and antifungal activities were also conducted using agar well diffusion method.
Results: The qualitative phytochemical analysis of hydro-alcoholic stem bark extracts of three plant species revealed the presence of various biochemical compounds such as alkaloids, flavonoids, glycosides, triterpenoids and saponins. Quantitative phytochemical analysis of plant extracts showed the presence of phenolics, flavonoids, tannins, beta-carotene and lycopene. Plant extracts of three pinus species showed significant antioxidant activity against DPPH, nitric oxide and H2O2 radicals. In in-vitro anti-inflammatory investigation, Pinus roxburghii exhibited highest protection against albumin denaturation 86.54 ± 1.85 whereas Pinus gerardiana showed 82.03 ± 2.67. Moreover, plant extracts were found to prevent the growth of microorganisms Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans showing promising antibacterial and antifungal activities againstCandida albicans.
Conclusion: The findings of the present study derived the rational for the therapeutic usage of Pinus which is a highly timber yielding plant from Himalayan region, against oxidative, inflammatory and microbial diseases.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chemical, antioxidant and antimicrobial investigations of Pinus cembra L. bark and needles.Molecules. 2011 Sep 13;16(9):7773-88. doi: 10.3390/molecules16097773. Molecules. 2011. PMID: 22143542 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial activity, toxicity and anti-inflammatory potential of methanolic extracts of four ethnomedicinal plant species from Punjab, Pakistan.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Jun 8;17(1):302. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1815-z. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28595608 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of optimal extraction, antioxidant, and antimicrobial activities of Achillea biebersteinii and A. wilhelmsii.Pharm Biol. 2012 Sep;50(9):1168-76. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2012.662235. Pharm Biol. 2012. PMID: 22881142
-
Ethnobotany and Pharmacology of Pinus Species Growing Naturally in Indian Himalayas: A Plant Review.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2019;20(15):1281-1287. doi: 10.2174/1389201020666190819153600. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31424365 Review.
-
Antibacterial, antifungal and antioxidant activity of total polyphenols of Withania frutescens.L.Bioorg Chem. 2019 Dec;93:103337. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103337. Epub 2019 Oct 8. Bioorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 31627061 Review.
Cited by
-
Studies of Phytochemicals, Antioxidant, and Antibacterial Activities of Pinus gerardiana and Pinus roxburghii Seed Extracts.Biomed Res Int. 2022 May 31;2022:5938610. doi: 10.1155/2022/5938610. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35686234 Free PMC article.
-
The Importance of Pine Species in the Ethnomedicine of Transylvania (Romania).Plants (Basel). 2022 Sep 6;11(18):2331. doi: 10.3390/plants11182331. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36145732 Free PMC article.
-
Prolonging Shelf Life and Meat Quality of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) by Immersing in Pine Nut (Pinus gerardiana) Extract During Cold Storage.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Dec 19;13(1):e4685. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4685. eCollection 2025 Jan. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39803226 Free PMC article.
-
In-vitro osteoblast proliferation and in-vivo anti-osteoporotic activity of Bombax ceiba with quantification of Lupeol, gallic acid and β-sitosterol by HPTLC and HPLC.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 Aug 7;18(1):233. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2299-1. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 30086745 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the Efficacy of Two Treatment Protocols for Patients with Symptomatic Oral Lichen Planus: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Dec 23;18(1):56. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18010056. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33374791 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Manian R, Anusuya N, Siddhuraju P, Manian S. The antioxidant activity and free radical scavenging potential of two different solvent extracts of Camellia sinensis, Ficus bengalensis and Ficus racemosa. Food Chem. 2008;107(3):1000–1007. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.09.008. - DOI
-
- Naskar S, Islam A, Mazumder UK, Saha P, Haldar PK, Gupta M. In Vitro and In Vivo Antioxidant Potential of Hydromethanolic Extract of Phoenix dactylifera. fruits. J Sci Res. 2010;2(1):144–157.
-
- Vogiatzi G, Tousoulis D, Stefanadis C. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Atherosclerosis. Hellenic J Cardiol. 2009;50:402–409. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

