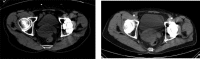
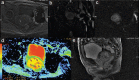
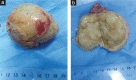
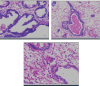
Rare primary seminal vesicle cystadenoma: computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging findings
- PMID: 26823068
- PMCID: PMC5427799
- DOI: 10.4103/1008-682X.173440
Rare primary seminal vesicle cystadenoma: computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging findings
Figures
Similar articles
-
Laparoscopic vesiculectomy for large seminal vesicle cystadenoma.Andrologia. 2019 Apr;51(3):e13209. doi: 10.1111/and.13209. Epub 2018 Nov 29. Andrologia. 2019. PMID: 30488974
-
Cystadenoma of the seminal vesicle: US and CT findings.Abdom Imaging. 1993;18(3):298-300. doi: 10.1007/BF00198130. Abdom Imaging. 1993. PMID: 8508100
-
Cystic schwannoma of a seminal vesicle.J Androl. 2012 Sep-Oct;33(5):798-800. doi: 10.2164/jandrol.111.015917. Epub 2012 Feb 23. J Androl. 2012. PMID: 22362077
-
Laparoscopic resection of a large mixed epithelial-stromal tumour of the seminal vesicle: a rare entity and review of the current literature.BMJ Case Rep. 2021 Feb 1;14(2):e238526. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2020-238526. BMJ Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 33526529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Cystadenoma of the seminal vesicles. A case report].Radiol Med. 1996 Mar;91(3):322-4. Radiol Med. 1996. PMID: 8628954 Review. Italian. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Multiple schwannoma of the seminal vesicle: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Aug 14;99(33):e21603. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000021603. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32872015 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gil AO, Yamakami LY, Genzini T. Cystadenoma of the seminal vesicle. Int Braz J Urol. 2003;29:434–6. - PubMed
-
- Lee CB, Choi HJ, Cho DH, Ha US. Cystadenoma of the seminal vesicle. Int J urol. 2006;13:1138–40. - PubMed
-
- Lorber G, Pizov G, Gofrit ON, Pode D. Seminal vesicle cystadenoma: a rare clinical perspective. Eur Urol. 2011;60:388–91. - PubMed
-
- Lagalla R, Zappasodi F, Lo Casto A, Zenico T. Cystadenoma of the seminal vesicle: US and CT findings. Abdom Imaging. 1993;18:298–300. - PubMed
-
- Arora A, Sharma S, Seth A. Unusual retrovesical cytic mass in a male patient. Urology. 2013;81:e23–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

