Non-invasive imaging of oxygen extraction fraction in adults with sickle cell anaemia
- PMID: 26823369
- PMCID: PMC5014126
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awv397
Non-invasive imaging of oxygen extraction fraction in adults with sickle cell anaemia
Abstract
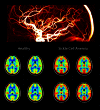
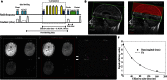
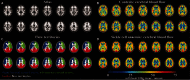
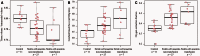
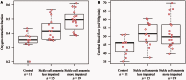
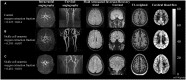
Sickle cell anaemia is a monogenetic disorder with a high incidence of stroke. While stroke screening procedures exist for children with sickle cell anaemia, no accepted screening procedures exist for assessing stroke risk in adults. The purpose of this study is to use novel magnetic resonance imaging methods to evaluate physiological relationships between oxygen extraction fraction, cerebral blood flow, and clinical markers of cerebrovascular impairment in adults with sickle cell anaemia. The specific goal is to determine to what extent elevated oxygen extraction fraction may be uniquely present in patients with higher levels of clinical impairment and therefore may represent a candidate biomarker of stroke risk. Neurological evaluation, structural imaging, and the non-invasive T2-relaxation-under-spin-tagging magnetic resonance imaging method were applied in sickle cell anaemia (n = 34) and healthy race-matched control (n = 11) volunteers without sickle cell trait to assess whole-brain oxygen extraction fraction, cerebral blood flow, degree of vasculopathy, severity of anaemia, and presence of prior infarct; findings were interpreted in the context of physiological models. Cerebral blood flow and oxygen extraction fraction were elevated (P < 0.05) in participants with sickle cell anaemia (n = 27) not receiving monthly blood transfusions (interquartile range cerebral blood flow = 46.2-56.8 ml/100 g/min; oxygen extraction fraction = 0.39-0.50) relative to controls (interquartile range cerebral blood flow = 40.8-46.3 ml/100 g/min; oxygen extraction fraction = 0.33-0.38). Oxygen extraction fraction (P < 0.0001) but not cerebral blood flow was increased in participants with higher levels of clinical impairment. These data provide support for T2-relaxation-under-spin-tagging being able to quickly and non-invasively detect elevated oxygen extraction fraction in individuals with sickle cell anaemia with higher levels of clinical impairment. Our results support the premise that magnetic resonance imaging-based assessment of elevated oxygen extraction fraction might be a viable screening tool for evaluating stroke risk in adults with sickle cell anaemia.
Keywords: arterial spin labelling; brain ischaemia; cerebral haemodynamics; oxygen extraction fraction; sickle cell anaemia.
© The Author (2016). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quantification of whole-brain oxygenation extraction fraction and cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen consumption in adults with sickle cell anemia using individual T2 -based oxygenation calibrations.Magn Reson Med. 2020 Mar;83(3):1066-1080. doi: 10.1002/mrm.27972. Epub 2019 Sep 4. Magn Reson Med. 2020. PMID: 31483528 Free PMC article.
-
Differential cerebral hemometabolic responses to blood transfusions in adults and children with sickle cell anemia.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019 Feb;49(2):466-477. doi: 10.1002/jmri.26213. Epub 2018 Oct 15. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30324698 Free PMC article.
-
Diminished cerebral oxygen extraction and metabolic rate in sickle cell disease using T2 relaxation under spin tagging MRI.Magn Reson Med. 2018 Jul;80(1):294-303. doi: 10.1002/mrm.27015. Epub 2017 Dec 1. Magn Reson Med. 2018. PMID: 29194727 Free PMC article.
-
Using novel magnetic resonance imaging methods to predict stroke risk in individuals with sickle cell anemia.Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2020 Jun;13(2):76-84. doi: 10.1016/j.hemonc.2019.12.009. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther. 2020. PMID: 32192979 Review.
-
Cerebral hemodynamic assessment and neuroimaging across the lifespan in sickle cell disease.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2018 Sep;38(9):1438-1448. doi: 10.1177/0271678X17701763. Epub 2017 Apr 18. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2018. PMID: 28417646 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Noise concerns and post-processing procedures in cerebral blood flow (CBF) and cerebral blood volume (CBV) functional magnetic resonance imaging.Neuroimage. 2017 Jul 1;154:43-58. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.09.007. Epub 2016 Sep 11. Neuroimage. 2017. PMID: 27622397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Validation of T2 -based oxygen extraction fraction measurement with 15 O positron emission tomography.Magn Reson Med. 2021 Jan;85(1):290-297. doi: 10.1002/mrm.28410. Epub 2020 Jul 8. Magn Reson Med. 2021. PMID: 32643207 Free PMC article.
-
Quantum Mimicry With Inorganic Chemistry.Comments Mod Chem A Comments Inorg Chem. 2024;44(1):11-53. doi: 10.1080/02603594.2023.2173588. Epub 2023 Feb 13. Comments Mod Chem A Comments Inorg Chem. 2024. PMID: 38515928 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Connectivity Decreases with Metabolic Stress in Sickle Cell Disease.Ann Neurol. 2020 Nov;88(5):995-1008. doi: 10.1002/ana.25891. Epub 2020 Sep 16. Ann Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32869335 Free PMC article.
-
White matter integrity and processing speed in sickle cell anemia.Neurology. 2018 Jun 5;90(23):e2042-e2050. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000005644. Epub 2018 May 11. Neurology. 2018. PMID: 29752305 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams RJ, McKie VC, Brambilla D, Carl E, Gallagher D, Nichols FT, et al. Stroke prevention trial in sickle cell anemia. Control Clin Trials 1998a; 19: 110–29. - PubMed
-
- Adams RJ, McKie VC, Hsu L, Files B, Vichinsky E, Pegelow C, et al. Prevention of a first stroke by transfusions in children with sickle cell anemia and abnormal results on transcranial Doppler ultrasonography. N Engl J Med 1998b; 339: 5–11. - PubMed
-
- Alsop DC, Detre JA, Golay X, Gunther M, Hendrikse J, Hernandez-Garcia L, et al. Recommended implementation of arterial spin-labeled perfusion MRI for clinical applications: A consensus of the ISMRM perfusion study group and the European consortium for ASL in dementia. Magn Reson Med 2015; 73: 102–16. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balkaran B, Char G, Morris JS, Thomas PW, Serjeant BE, Serjeant GR. Stroke in a cohort of patients with homozygous sickle cell disease. J Pediatr 1992; 120: 360–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

