An unprecedented mechanism of nucleotide methylation in organisms containing thyX
- PMID: 26823429
- PMCID: PMC4744818
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aad0300
An unprecedented mechanism of nucleotide methylation in organisms containing thyX
Abstract
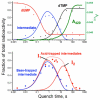
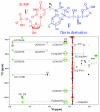
In several human pathogens, thyX-encoded flavin-dependent thymidylate synthase (FDTS) catalyzes the last step in the biosynthesis of thymidylate, one of the four DNA nucleotides. ThyX is absent in humans, rendering FDTS an attractive antibiotic target; however, the lack of mechanistic understanding prohibits mechanism-based drug design. Here, we report trapping and characterization of two consecutive intermediates, which together with previous crystal structures indicate that the enzyme's reduced flavin relays a methylene from the folate carrier to the nucleotide acceptor. Furthermore, these results corroborate an unprecedented activation of the nucleotide that involves no covalent modification but only electrostatic polarization by the enzyme's active site. These findings indicate a mechanism that is very different from thymidylate biosynthesis in humans, underscoring the promise of FDTS as an antibiotic target.
Copyright © 2016, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures


Similar articles
-
An unusual mechanism of thymidylate biosynthesis in organisms containing the thyX gene.Nature. 2009 Apr 16;458(7240):919-23. doi: 10.1038/nature07973. Nature. 2009. PMID: 19370033 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Plasticity of Flavin-Dependent Thymidylate Synthase Controlled by the Enzyme Redox State.Biomolecules. 2025 Feb 21;15(3):318. doi: 10.3390/biom15030318. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40149854 Free PMC article.
-
Folate binding site of flavin-dependent thymidylate synthase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Sep 25;109(39):15722-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1206077109. Epub 2012 Sep 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23019356 Free PMC article.
-
Flavin-dependent thymidylate synthase: N5 of flavin as a Methylene carrier.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2017 Oct 15;632:11-19. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2017.08.011. Epub 2017 Aug 15. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2017. PMID: 28821425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two distinct pathways for thymidylate (dTMP) synthesis in (hyper)thermophilic Bacteria and Archaea.Biochem Soc Trans. 2004 Apr;32(Pt 2):231-5. doi: 10.1042/bst0320231. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004. PMID: 15046578 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemo-enzymatic synthesis of the exocyclic olefin isomer of thymidine monophosphate.Bioorg Med Chem. 2018 May 15;26(9):2365-2371. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2018.03.032. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Bioorg Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29606487 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and structural characterization of meningococcal methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase.Protein Sci. 2023 Jun;32(6):e4654. doi: 10.1002/pro.4654. Protein Sci. 2023. PMID: 37165541 Free PMC article.
-
Deprotonations in the Reaction of Flavin-Dependent Thymidylate Synthase.Biochemistry. 2016 Jun 14;55(23):3261-9. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00510. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Biochemistry. 2016. PMID: 27214228 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic Changes in Active Site Polarization and Dynamics Drive the 'Ping-pong' Kinetics in NRH:Quinone Oxidoreductase 2: An Insight from QM/MM Simulations.ACS Catal. 2018 Dec 7;8(12):12015-12029. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.8b04193. Epub 2018 Nov 14. ACS Catal. 2018. PMID: 31583178 Free PMC article.
-
Flavin-Dependent Thymidylate Synthase as a New Antibiotic Target.Molecules. 2016 May 20;21(5):654. doi: 10.3390/molecules21050654. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27213314 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Myllykallio H, et al. An alternative flavin-dependent mechanism for thymidylate synthesis. Science. 2002;297:105–107. - PubMed
-
- Leduc D, et al. Two distinct pathways for thymidylate (dTMP) synthesis in (hyper)thermophilic Bacteria and Archaea. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2004;32:231–235. - PubMed
-
- Mathews II, et al. Functional analysis of substrate and cofactor complex structures of a thymidylate-synthase complementing protein. Structure (Camb.) 2003;11:677–690. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

