Intrathecal Injections in Children With Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Nusinersen Clinical Trial Experience
- PMID: 26823478
- PMCID: PMC4871174
- DOI: 10.1177/0883073815627882
Intrathecal Injections in Children With Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Nusinersen Clinical Trial Experience
Abstract
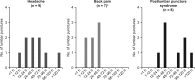
Nusinersen (ISIS-SMNRx or ISIS 396443) is an antisense oligonucleotide drug administered intrathecally to treat spinal muscular atrophy. We summarize lumbar puncture experience in children with spinal muscular atrophy during a phase 1 open-label study of nusinersen and its extension. During the studies, 73 lumbar punctures were performed in 28 patients 2 to 14 years of age with type 2/3 spinal muscular atrophy. No complications occurred in 50 (68%) lumbar punctures; in 23 (32%) procedures, adverse events were attributed to lumbar puncture. Most common adverse events were headache (n = 9), back pain (n = 9), and post-lumbar puncture syndrome (n = 8). In a subgroup analysis, adverse events were more frequent in older children, children with type 3 spinal muscular atrophy, and with a 21- or 22-gauge needle compared to a 24-gauge needle or smaller. Lumbar punctures were successfully performed in children with spinal muscular atrophy; lumbar puncture-related adverse event frequency was similar to that previously reported in children.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01494701 NCT01780246.
Keywords: antisense oligonucleotide; drug delivery; lumbar puncture; spinal muscular atrophy.
© The Author(s) 2016.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Multiple sclerosis. Management of multiple sclerosis in primary and secondary care. NICE Guidance. Published November 2003. - PubMed
-
- Crawford TO, Pardo CA. The neurobiology of childhood spinal muscular atrophy. Neurobiol Dis. 1996;3:97–110. - PubMed
-
- Lefebvre S, Burglen L, Reboullet S, et al. Identification and characterization of a spinal muscular atrophy-determining gene. Cell. 1995;80:155–165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical