Posaconazole, a Second-Generation Triazole Antifungal Drug, Inhibits the Hedgehog Signaling Pathway and Progression of Basal Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 26823493
- PMCID: PMC4873341
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0729-T
Posaconazole, a Second-Generation Triazole Antifungal Drug, Inhibits the Hedgehog Signaling Pathway and Progression of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
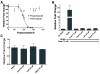
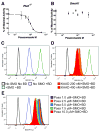
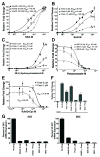
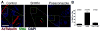
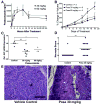
Deregulation of Hedgehog (Hh) pathway signaling has been associated with the pathogenesis of various malignancies, including basal cell carcinomas (BCC). Inhibitors of the Hh pathway currently available or under clinical investigation all bind and antagonize Smoothened (SMO), inducing a marked but transient clinical response. Tumor regrowth and therapy failure were attributed to mutations in the binding site of these small-molecule SMO antagonists. The antifungal itraconazole was demonstrated to be a potent SMO antagonist with a distinct mechanism of action from that of current SMO inhibitors. However, itraconazole represents a suboptimal therapeutic option due to its numerous drug-drug interactions. Here, we show that posaconazole, a second-generation triazole antifungal with minimal drug-drug interactions and a favorable side-effect profile, is also a potent inhibitor of the Hh pathway that functions at the level of SMO. We demonstrate that posaconazole inhibits the Hh pathway by a mechanism distinct from that of cyclopamine and other cyclopamine-competitive SMO antagonists but, similar to itraconazole, has robust activity against drug-resistant SMO mutants and inhibits the growth of Hh-dependent BCC in vivo Our results suggest that posaconazole, alone or in combination with other Hh pathway antagonists, may be readily tested in clinical studies for the treatment of Hh-dependent cancers. Mol Cancer Ther; 15(5); 866-76. ©2016 AACR.
©2016 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: E.H.E. is a founder and member of the Board of Directors for PellePharm Inc. The other authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
DYRK1B as therapeutic target in Hedgehog/GLI-dependent cancer cells with Smoothened inhibitor resistance.Oncotarget. 2016 Feb 9;7(6):7134-48. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6910. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26784250 Free PMC article.
-
A novel indole derivative, 2-{3-[1-(benzylsulfonyl)piperidin-4-yl]-2-methyl-1H-indol-1-yl}-1-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)ethenone, suppresses hedgehog signaling and drug-resistant tumor growth.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2024 Oct;357(10):e2400218. doi: 10.1002/ardp.202400218. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2024. PMID: 38963677
-
Discovery of [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyridines as potent Smoothened inhibitors targeting the Hedgehog pathway with improved antitumor activity in vivo.Bioorg Med Chem. 2020 Aug 15;28(16):115584. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115584. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Bioorg Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32690258
-
Small Molecule Inhibitors of the Hedgehog Pathway in the Treatment of Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Skin.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018 Apr;19(2):195-207. doi: 10.1007/s40257-017-0319-4. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 28887802 Review.
-
Targeting the hedgehog pathway to treat basal cell carcinoma.J Drugs Dermatol. 2013 May;12(5):519-23. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013. PMID: 23652945 Review.
Cited by
-
Cytotoxic and targeted therapy for hereditary cancers.Hered Cancer Clin Pract. 2016 Aug 23;14(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13053-016-0057-2. eCollection 2016. Hered Cancer Clin Pract. 2016. PMID: 27555886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Potent Zika Virus NS5 RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Inhibitors Combining Virtual Screening and Biological Assays.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 18;24(3):1900. doi: 10.3390/ijms24031900. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768218 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel, Rapid, and Low-Volume Assay for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Posaconazole and Other Long-Chain Azole-Class Antifungal Drugs.mSphere. 2018 Dec 19;3(6):e00623-18. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00623-18. mSphere. 2018. PMID: 30567902 Free PMC article.
-
Sterol regulation of developmental and oncogenic Hedgehog signaling.Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 Feb;196:114647. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114647. Epub 2021 Jun 7. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34111427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biallelic PTCH1 Inactivation Is a Dominant Genomic Change in Sporadic Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumors.Am J Surg Pathol. 2020 Apr;44(4):553-560. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000001407. Am J Surg Pathol. 2020. PMID: 31725470 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gorlin RJ. Nevoid basal-cell carcinoma syndrome. Medicine (Baltimore) 1987;66:98–113. - PubMed
-
- Sasai N, Briscoe J. Primary cilia and graded Sonic Hedgehog signaling. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2012;1:753–72. - PubMed
-
- Cooper MK, Porter JA, Young KE, Beachy PA. Teratogen-mediated inhibition of target tissue response to Shh signaling. Science. 1998;280:1603–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

