Prostate Cancer Susceptibility in Men of African Ancestry at 8q24
- PMID: 26823525
- PMCID: PMC4948565
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djv431
Prostate Cancer Susceptibility in Men of African Ancestry at 8q24
Abstract
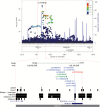
The 8q24 region harbors multiple risk variants for distinct cancers, including >8 for prostate cancer. In this study, we conducted fine mapping of the 8q24 risk region (127.8-128.8Mb) in search of novel associations with common and rare variation in 4853 prostate cancer case patients and 4678 control subjects of African ancestry. All statistical tests were two-sided. We identified three independent associations at P values of less than 5.00×10(-8), all of which were replicated in studies from Ghana and Uganda (combined sample = 5869 case patients, 5615 control subjects; rs114798100: risk allele frequency [RAF] = 0.04, per-allele odds ratio [OR] = 2.31, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 2.04 to 2.61, P = 2.38×10(-40); rs72725879: RAF = 0.33, OR = 1.37, 95% CI = 1.30 to 1.45, P = 3.04×10(-27); and rs111906932: RAF = 0.03, OR = 1.79, 95% CI = 1.53 to 2.08, P = 1.39×10(-13)). Risk variants rs114798100 and rs111906923 are only found in men of African ancestry, with rs111906923 representing a novel association signal. The three variants are located within or near a number of prostate cancer-associated long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), including PRNCR1, PCAT1, and PCAT2. These findings highlight ancestry-specific risk variation and implicate prostate-specific lncRNAs at the 8q24 prostate cancer susceptibility region.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Amundadottir LT, Sulem P, Gudmundsson J, et al. A common variant associated with prostate cancer in European and African populations. Nat Genet. 2006;38( 6):652–658. - PubMed
-
- Takata R, Akamatsu S, Kubo M, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies five new susceptibility loci for prostate cancer in the Japanese population. Nat Genet. 2010;42( 9):751–754. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA54281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-PC-35139/PC/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA056678/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA082664/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U58 DP000807/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- CA148085/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA063464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA082664/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA088164/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA140388/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA092447/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA68485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES011126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA092579/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA182883/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA165862/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004726/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 CA148085/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ES007784/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- 1U58DP000807-03/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- CA88164/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA180995/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA127298/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA092579/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037429/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA136924/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA1326792/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA165862/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA140388/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5UM1CA182883/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA127298/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189974/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 PC035139/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA37429/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA068578/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HG004726/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- CA68578/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA056678/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA63464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES007784/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA054281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA063464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

