Assessing the efficacy and safety of combined DPP-4 inhibitor and insulin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 26823727
- PMCID: PMC4713513
Assessing the efficacy and safety of combined DPP-4 inhibitor and insulin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis
Abstract
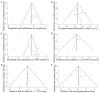
The use of DPP-4 inhibitors in combination with insulin has been proposed as an alternative therapeutic option for poorly controlled type 2 diabetes (T2D) patients. We thus performed a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to assess the efficacy and safety of this combination therapy in adult T2D patients. Seven eligible studies involving 3,384 participants were included for the study. The resulting data revealed that the combination therapy of DPP-4 inhibitor and insulin is associated with a modest reduction in HbA1c (-0.52%; 95% CI -0.59 to -0.44), a decrease in 2h-PPG (-1.81 mmol/l; -2.23 to -1.38), and an increase in the proportion of patients reaching the target HbA1c of ≤ 7% (RR 2.24; 95% CI 1.80 to 2.77) without increasing the risk of hypoglycemia (RR 1.04; 0.83 to 1.31) or body weight (-0.11 kg; -0.56 to 0.33), as compared with other anti-diabetic treatments. These results support that this combination therapy could serve as a potential therapeutic strategy that offers an alternative option for patients inadequately controlled on other anti-diabetic agents in clinical practice.
Keywords: DPP-4 inhibitors; hypoglycemia; insulin; type 2 diabetes; weight gain.
Figures



References
-
- DeFronzo RA. Pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Med Clin North Am. 2004;88:787–835. ix. - PubMed
-
- Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, Peters AL, Tsapas A, Wender R, Matthews DR American Diabetes Association (ADA); European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a patientcentered approach: position statement of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) Diabetes Care. 2012;35:1364–1379. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Turner RC, Cull CA, Frighi V, Holman RR. Glycemic control with diet, sulfonylurea, metformin, or insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: progressive requirement for multiple therapies (UKPDS 49). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. JAMA. 1999;281:2005–2012. - PubMed
-
- Korytkowski M. When oral agents fail: practical barriers to starting insulin. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2002;26(Suppl 3):S18–24. - PubMed
-
- Guler S, Vaz JA, Ligthelm R. Intensification lessons with modern premixes: from clinical trial to clinical practice. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2008;81(Suppl 1):S23–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
